This apparent surge in wildfire activity has caused growing concern about wildfire risk around the world and has led some to ask whether large and destructive megafires are becoming the new normal.
In The Burning Issue: Managing Wildfire Risk, Marsh & McLennan Insights examines the global outlook for wildfire risk in the context of climate change and urban expansions into fire-prone wildlands. The report addresses the total cost of wildfires as well as the drivers of wildfire risk and the outlook in key regions of the world. It concludes with a series of recommendations for how wildfire risk can be managed.
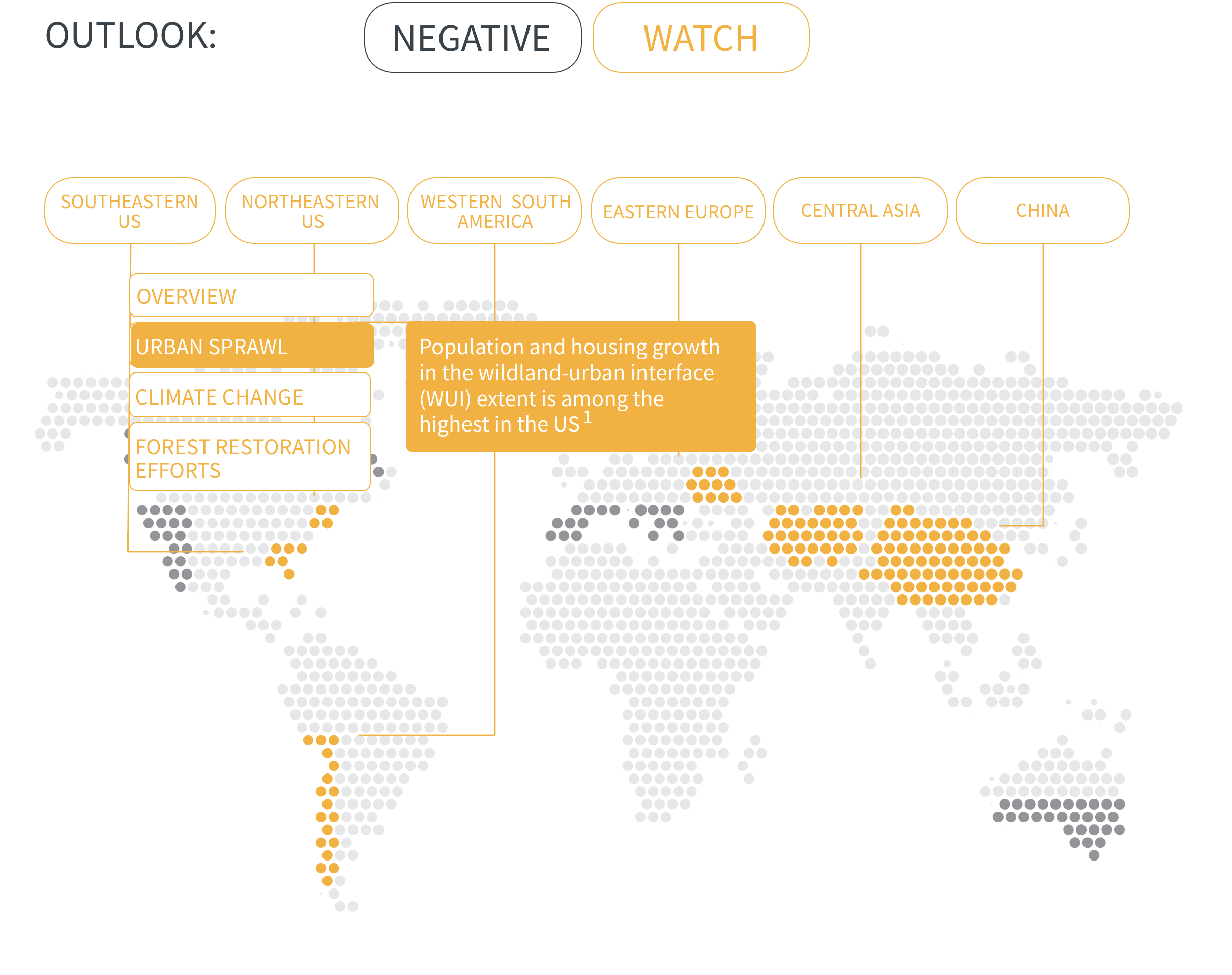
Urban expansion into wildlands is growing at a rapid pace and exposing more people and assets to wildfire
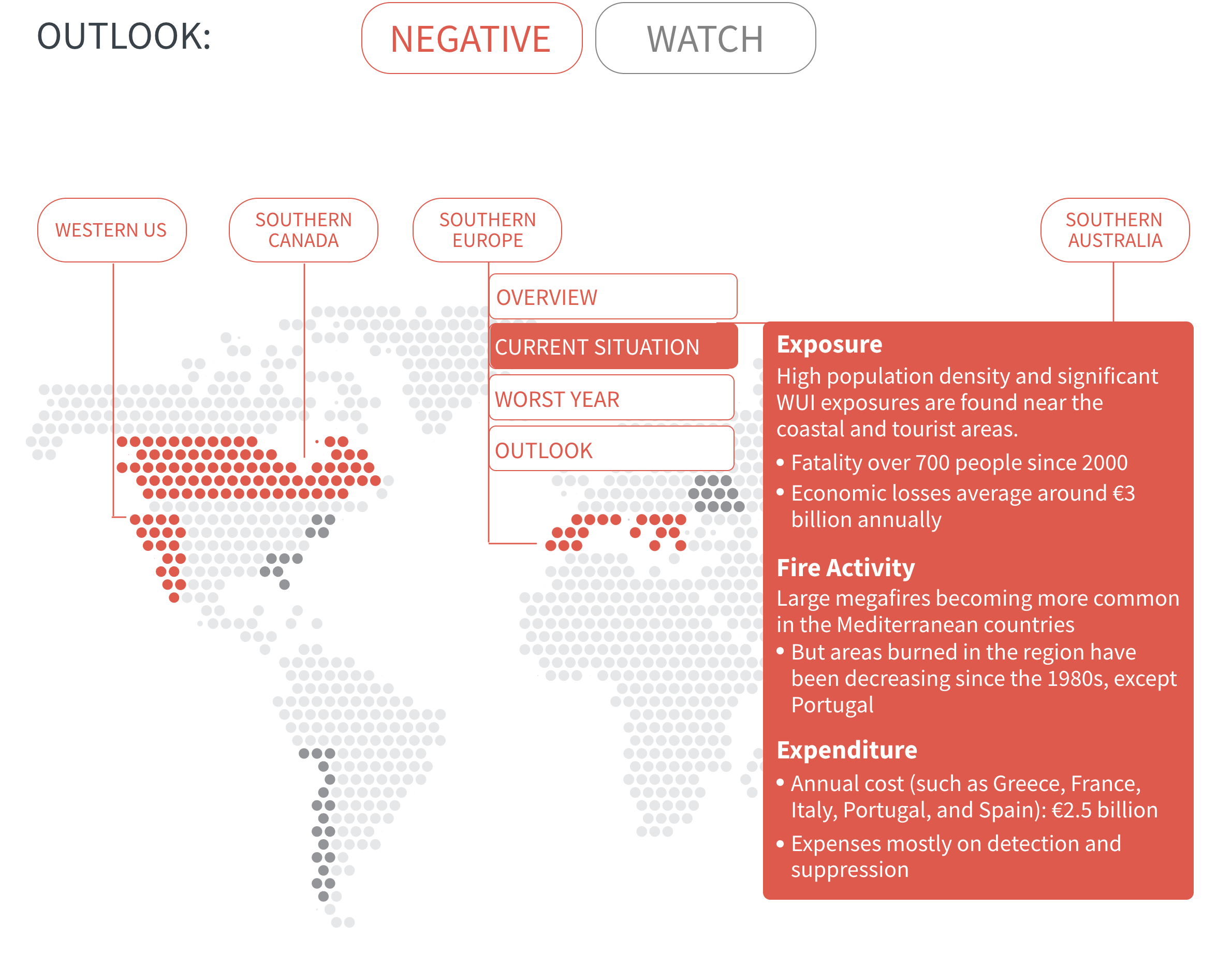
The total costs of wildfires are often much greater than immediately apparent
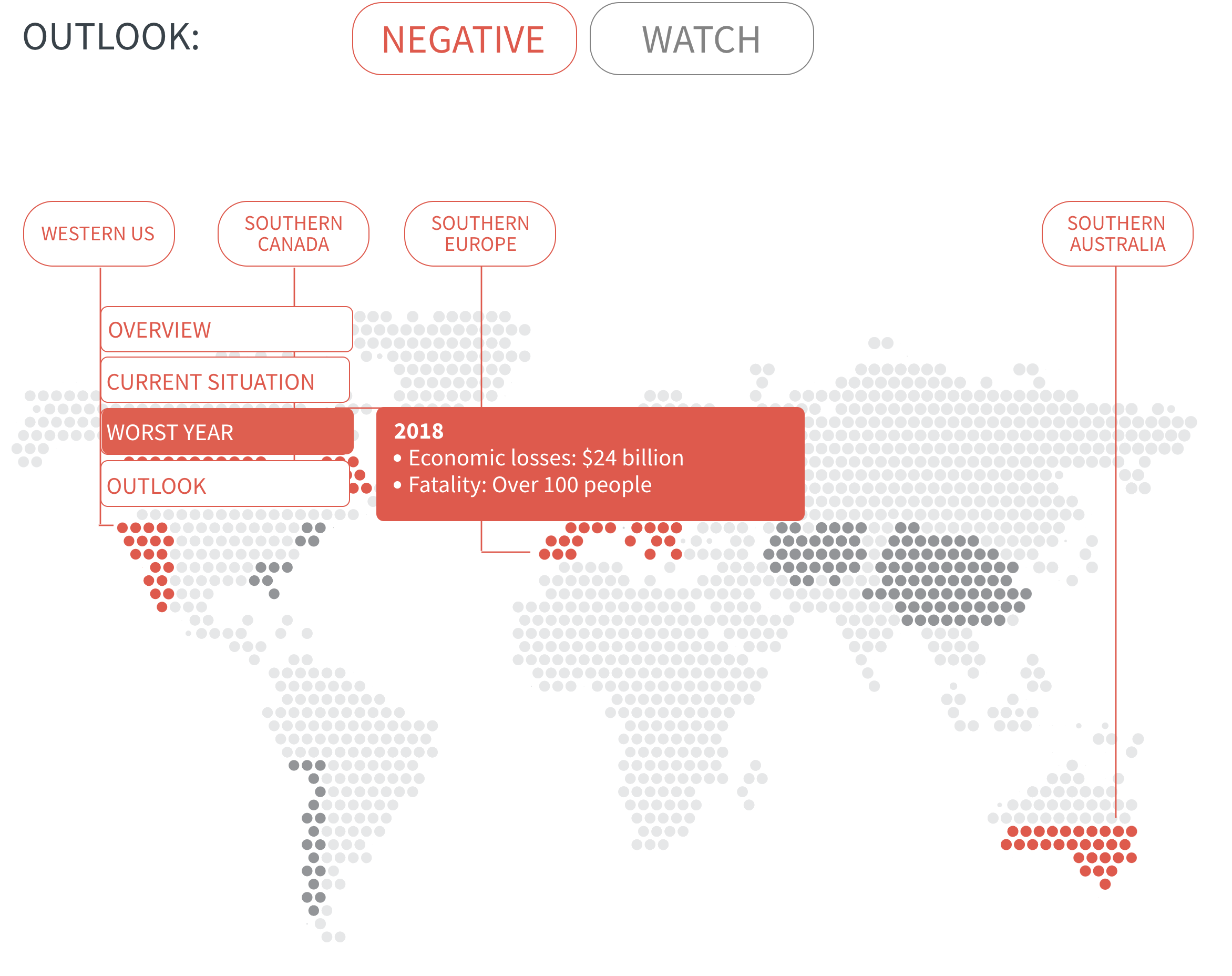
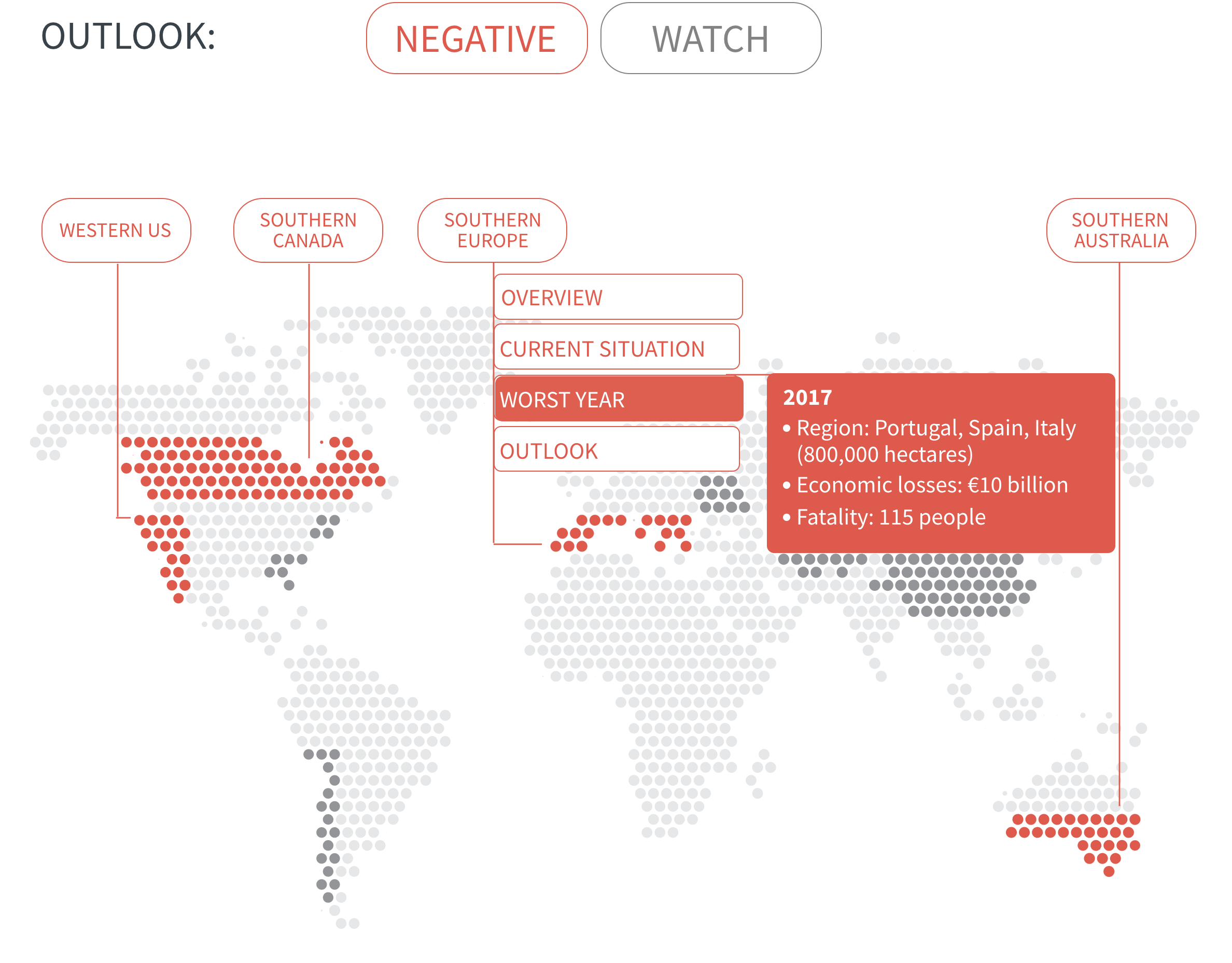
Both 2017 and 2018 witnessed record-breaking economic losses from wildfires – over $20 billion annually, driven by catastrophic fire seasons in California. However, these direct losses are likely to reflect only a fraction of the full costs, as they exclude firefighting costs and wider societal (such as deteriorating air pollution and public health) and environmental damage (such as greater greenhouse gas emissions).
Underlying drivers point to increasing risk: climate change and urban expansion
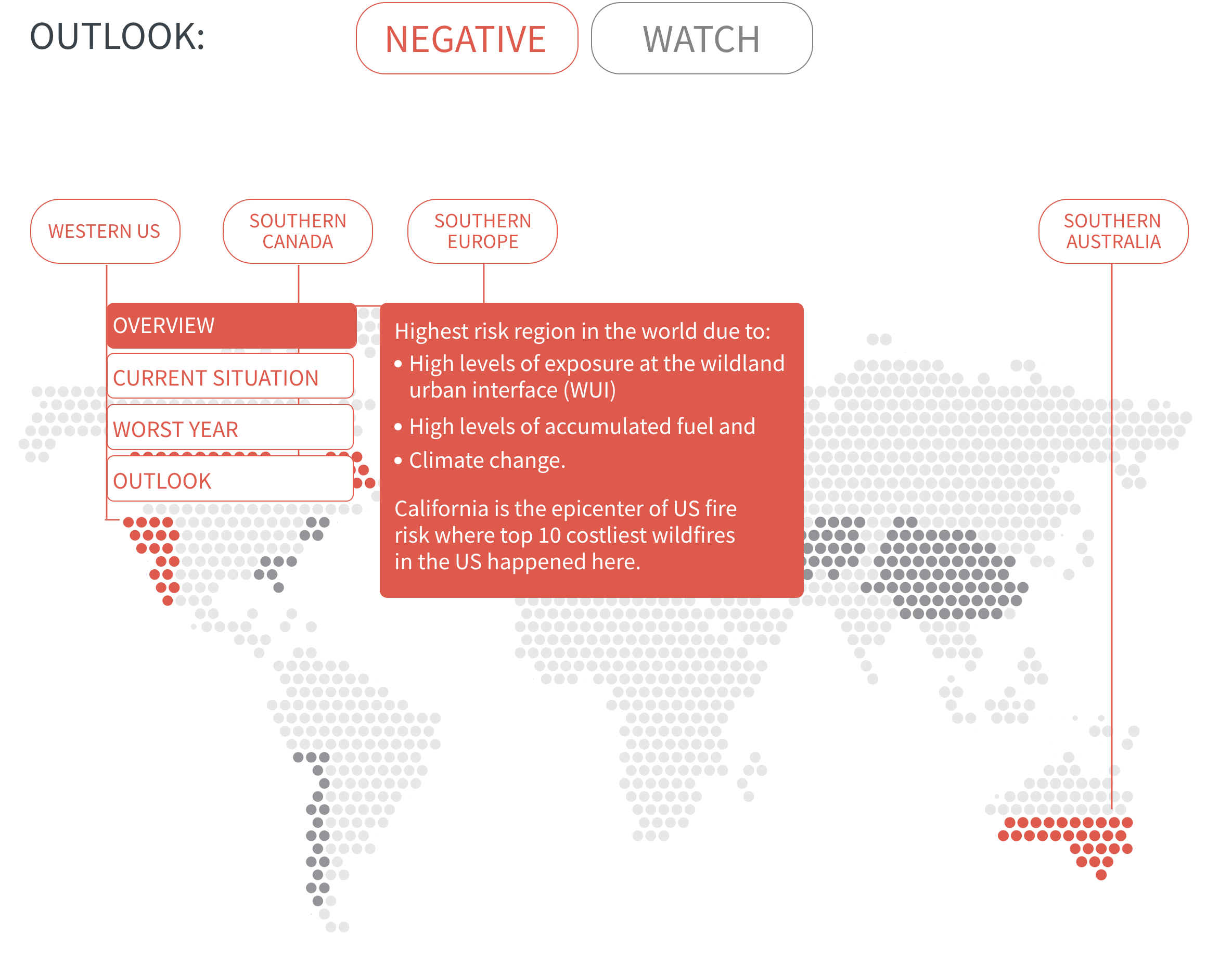
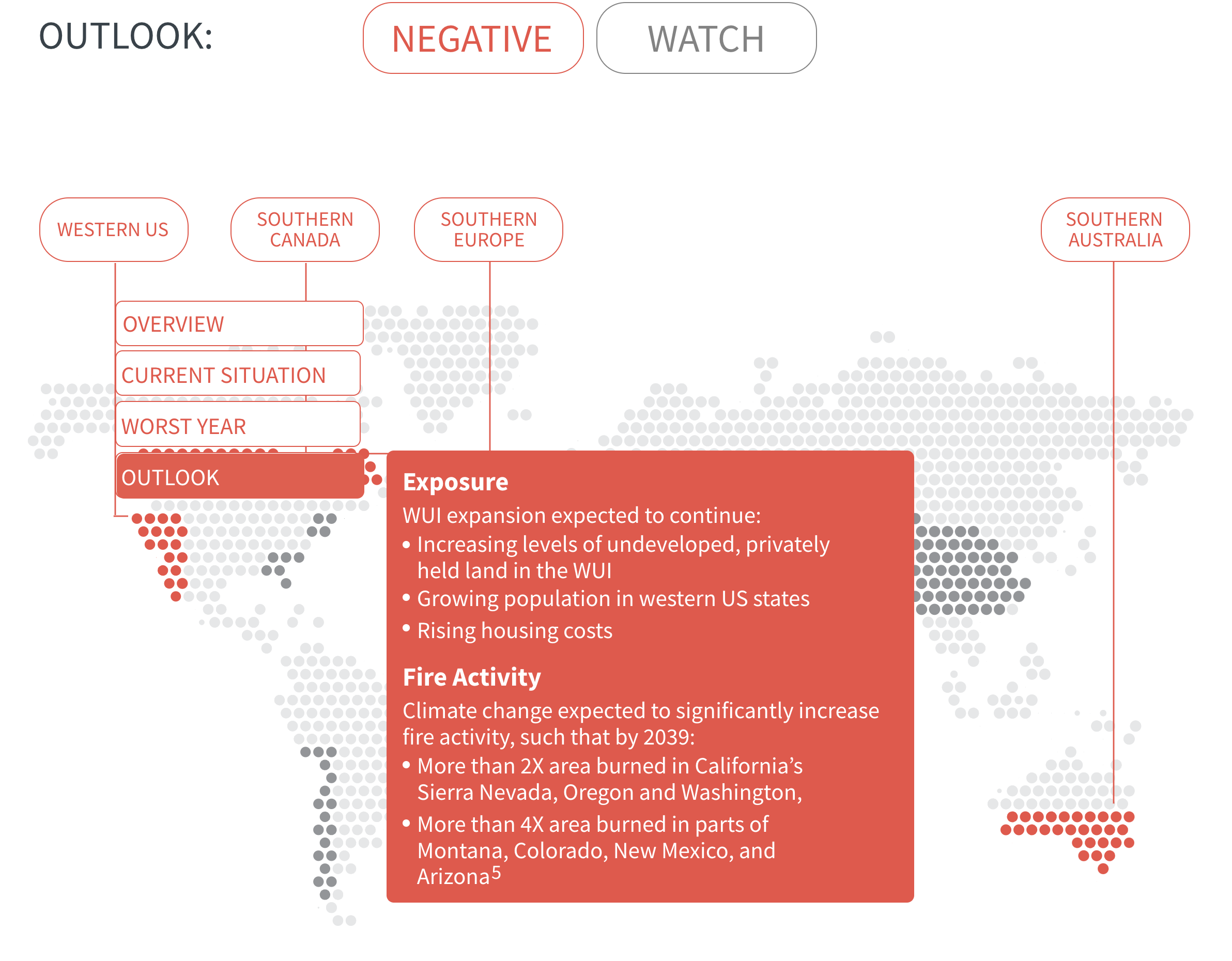
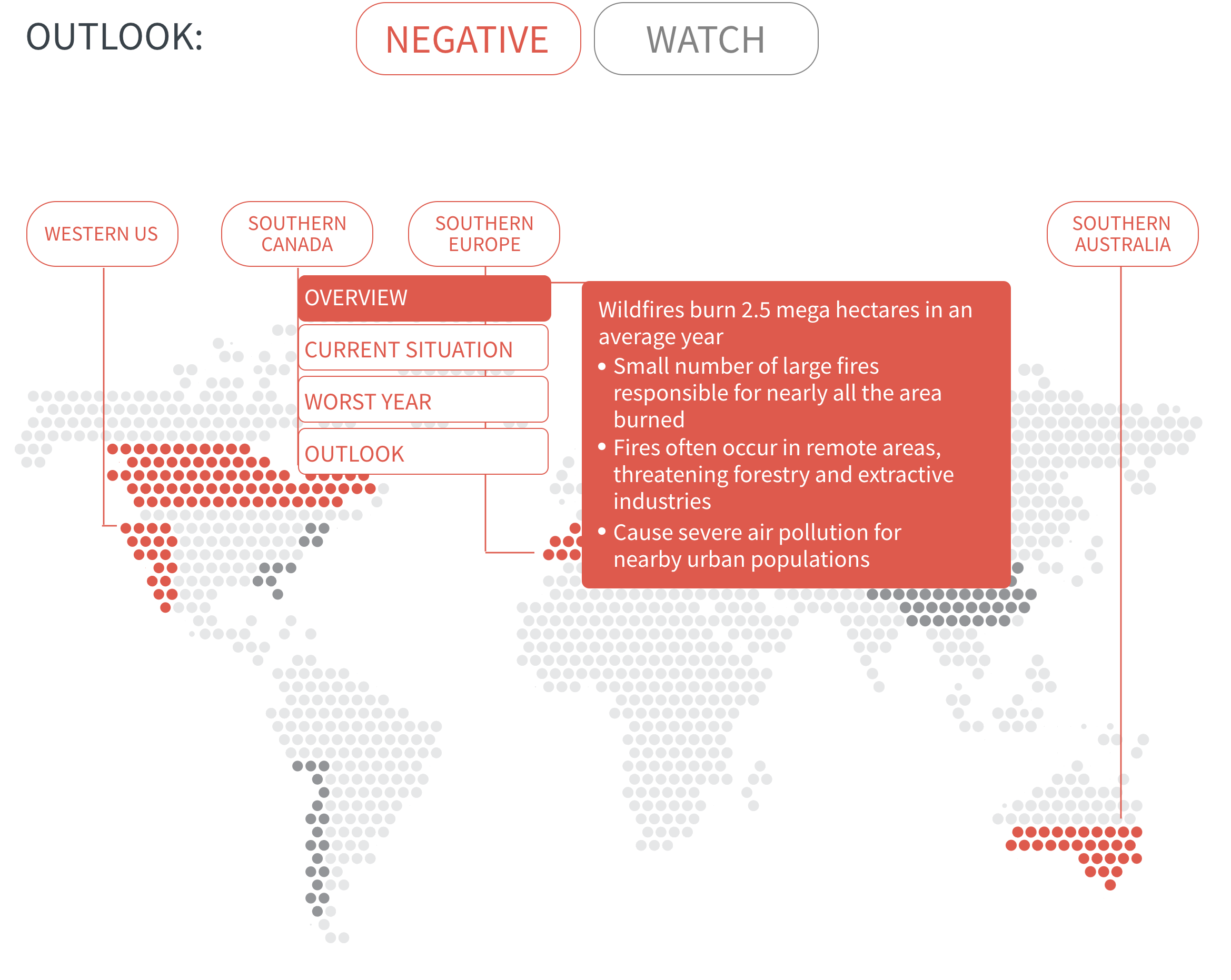
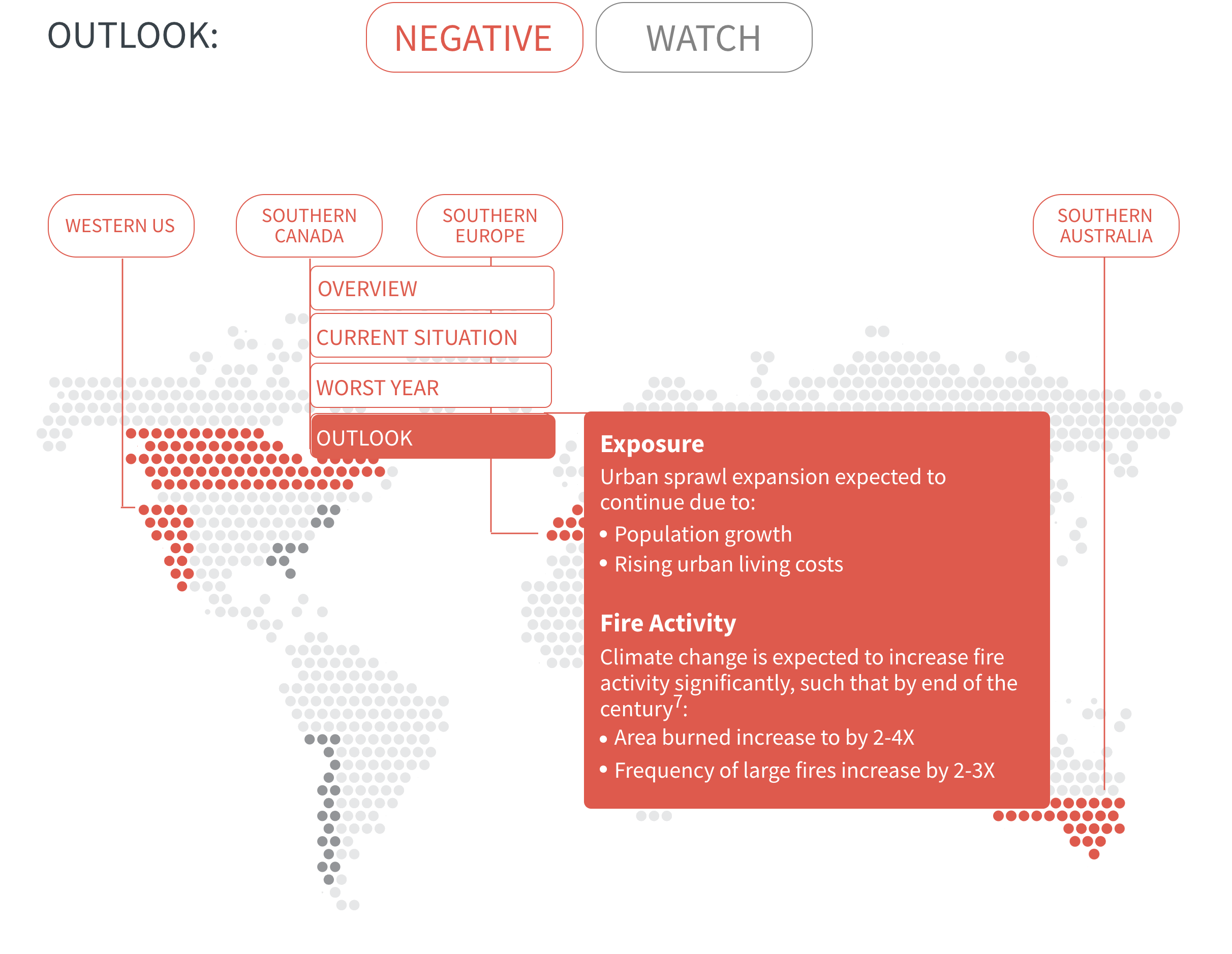
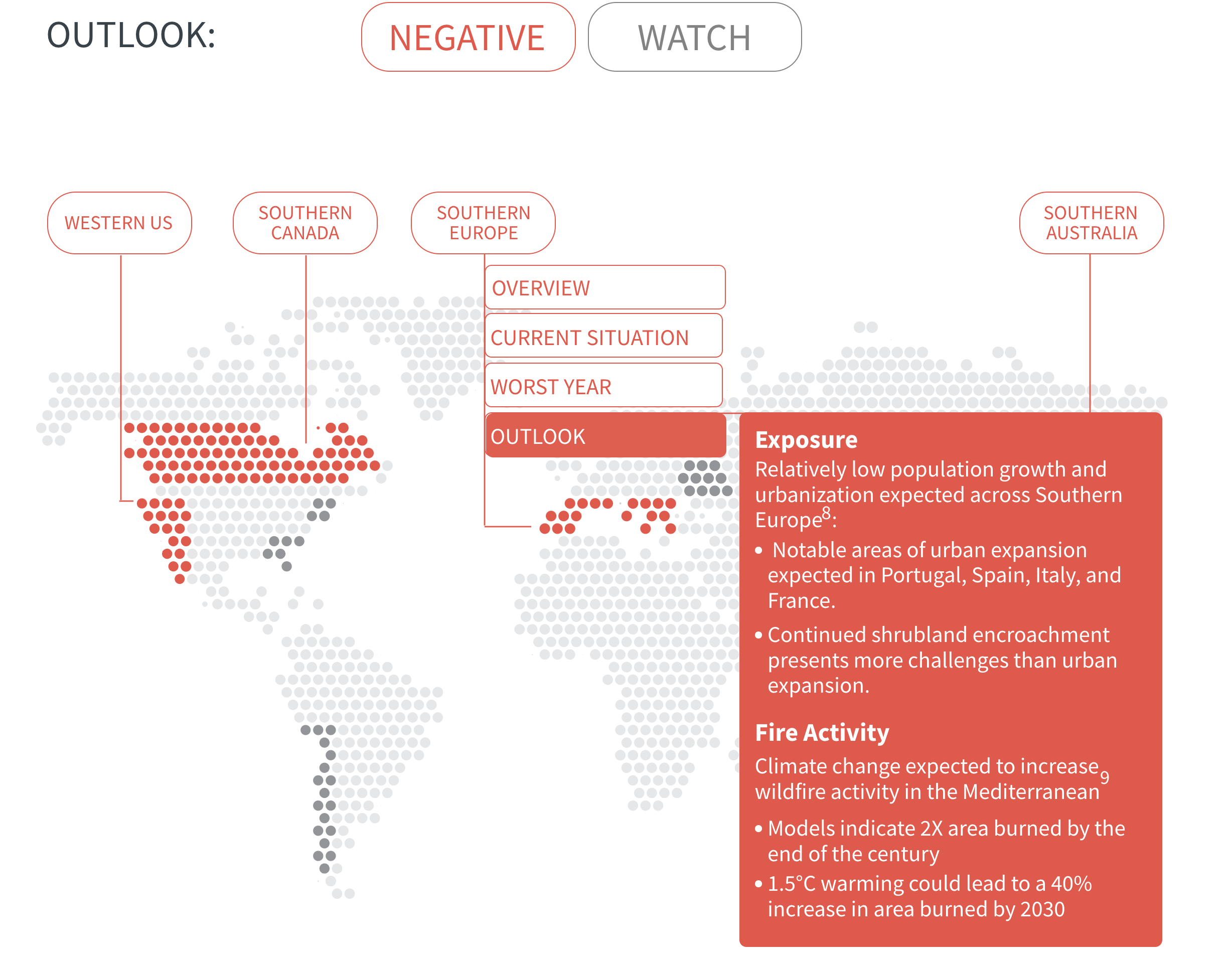
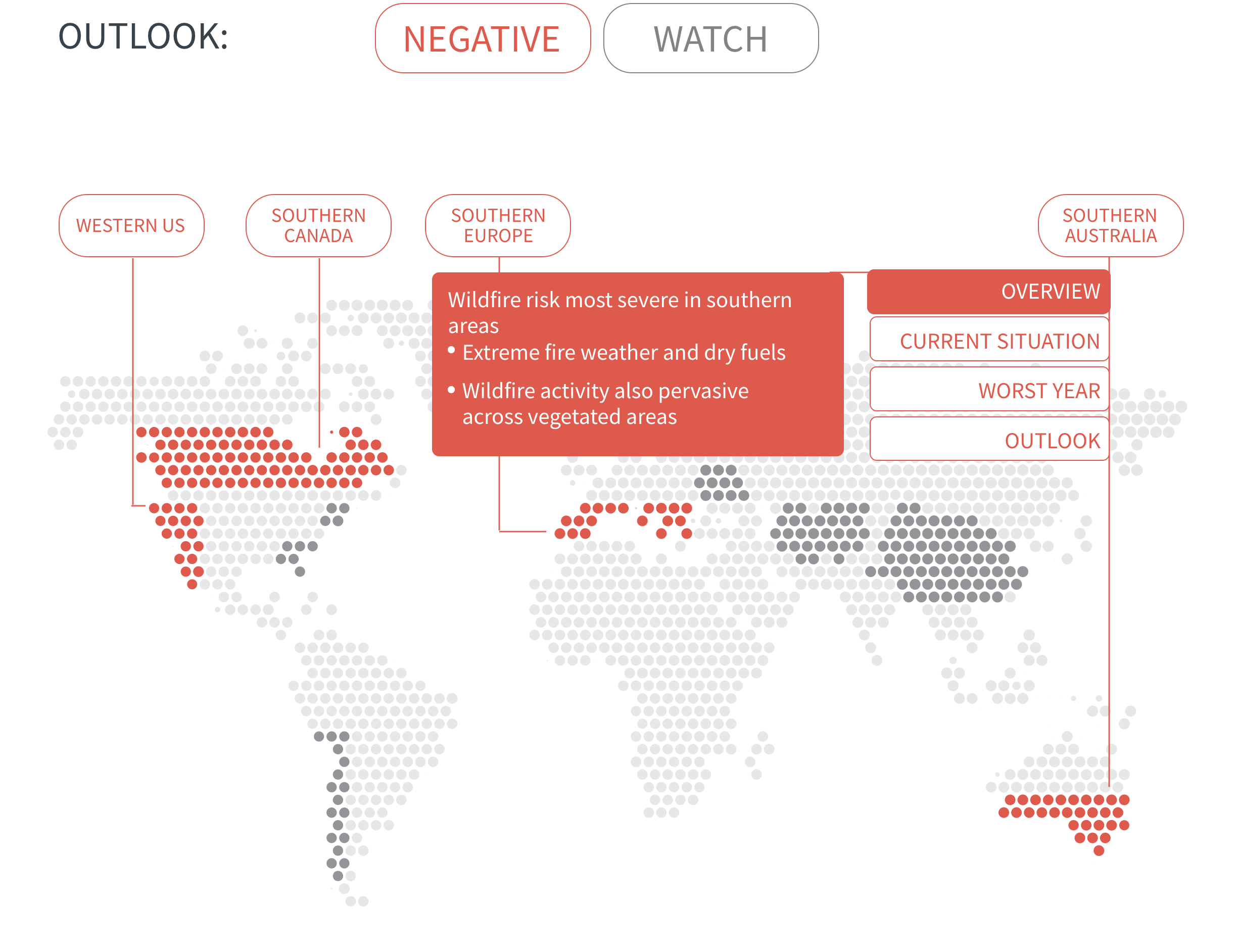
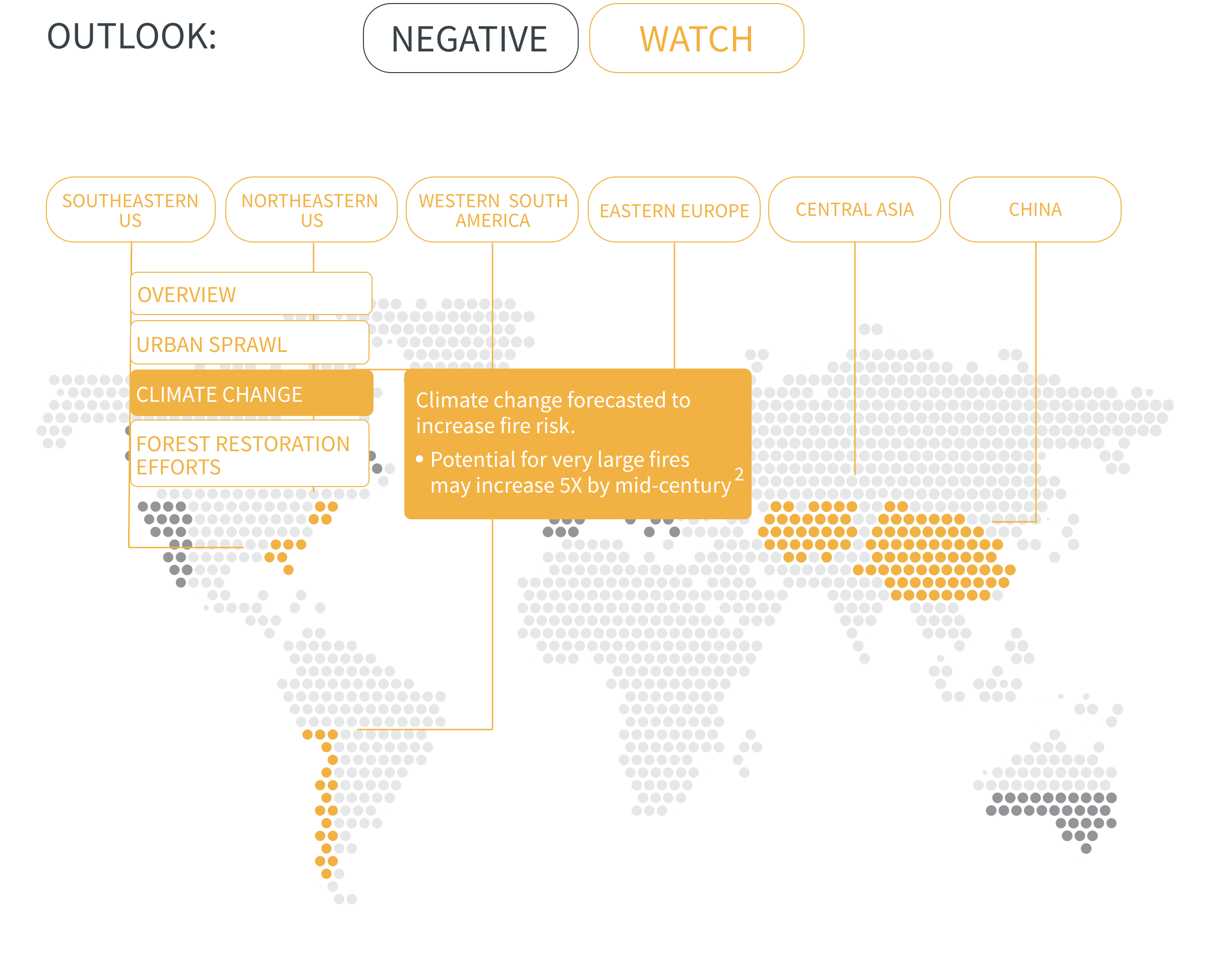
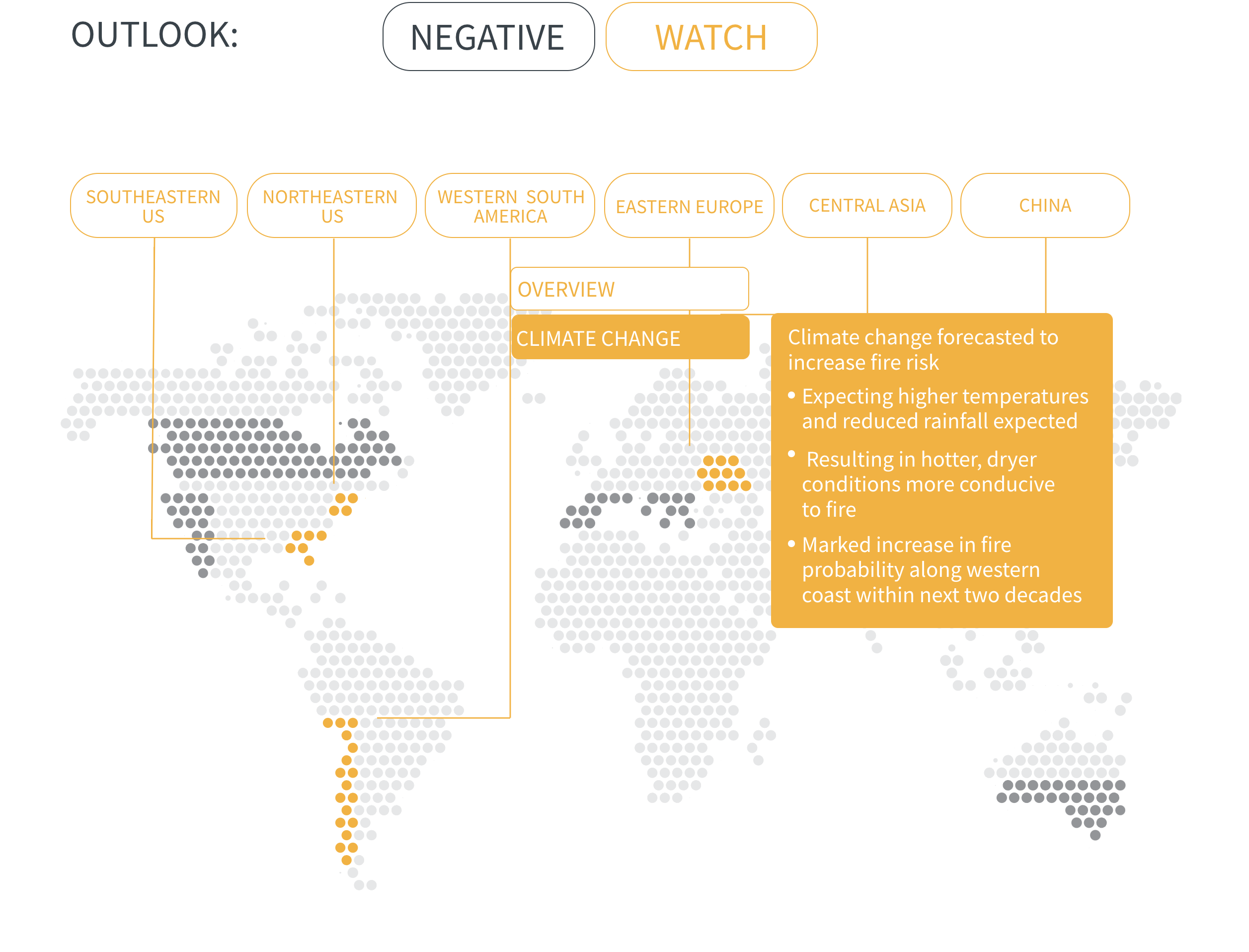
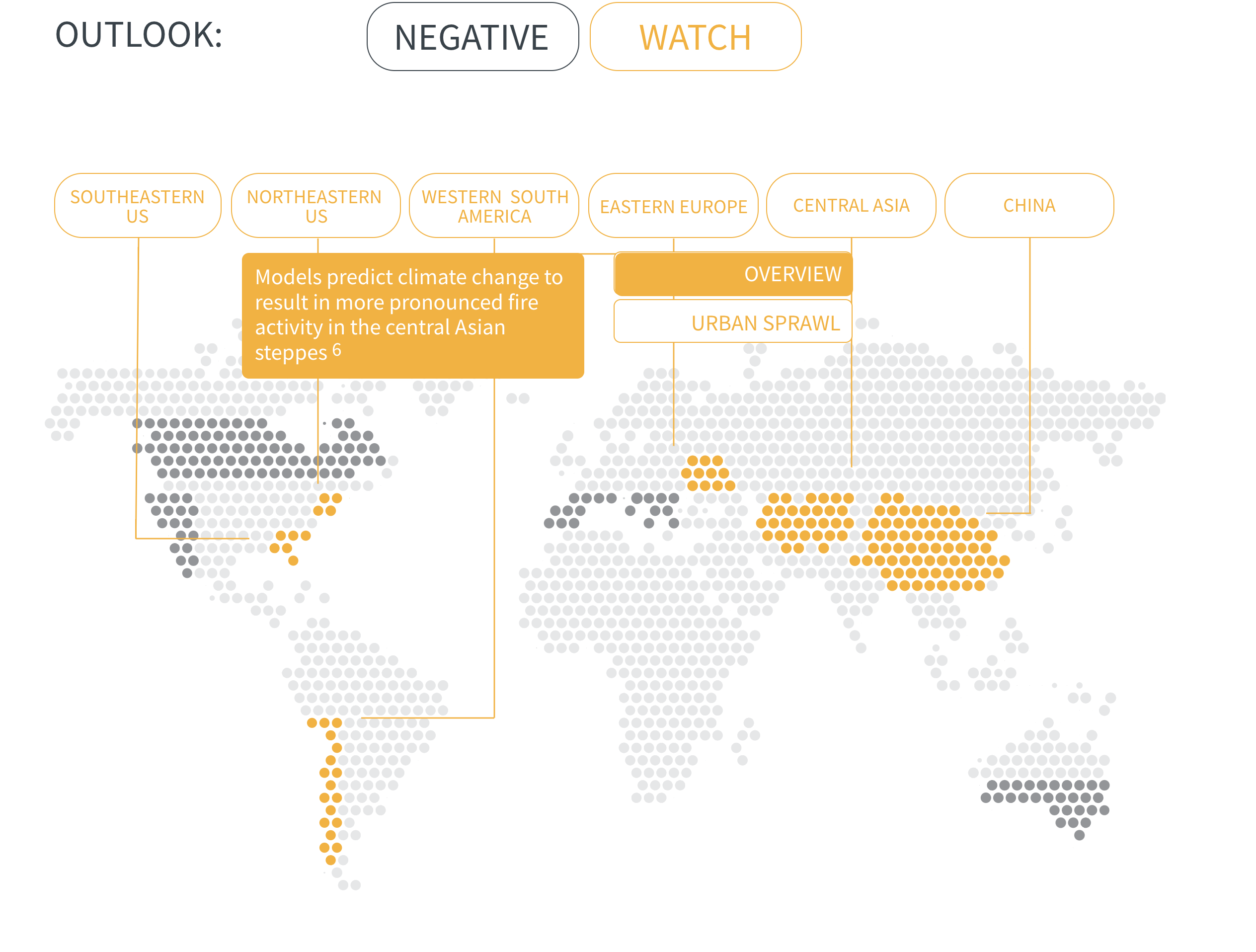
In many regions, climate change is increasing the likelihood of hot and dry conditions in which wildfires thrive. Fire seasons have already lengthened around the world, and modelling predicts significant increases in fire activity in high-risk areas such as southern Canada, western US and southern Europe.
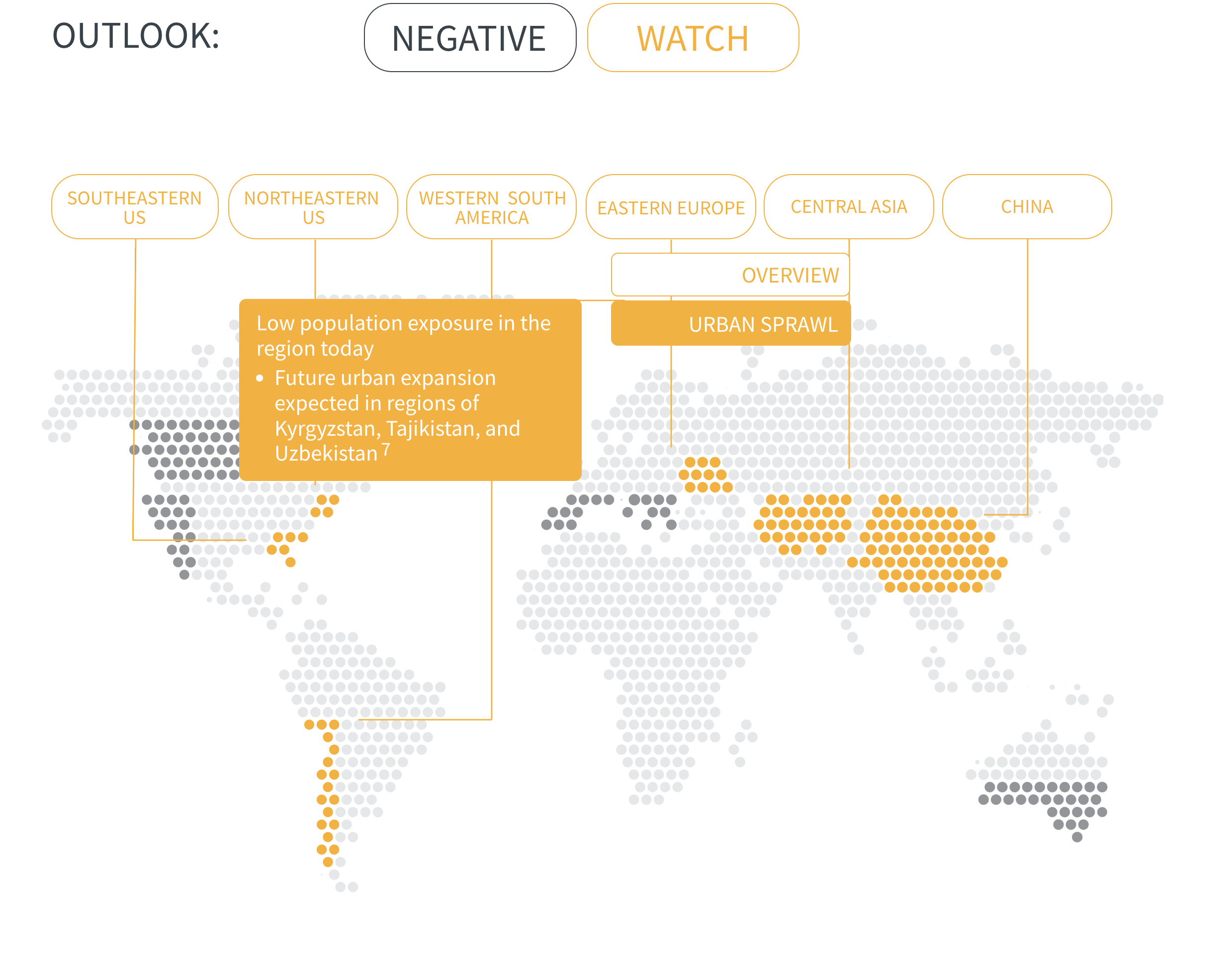
Meanwhile, urban expansion into wildlands is growing at a rapid pace and exposing more people and assets to wildfire. It also introduces a new cause of ignition—people—into fire-prone areas. For instance, in densely populated Europe, nearly all wildfires are started by people.
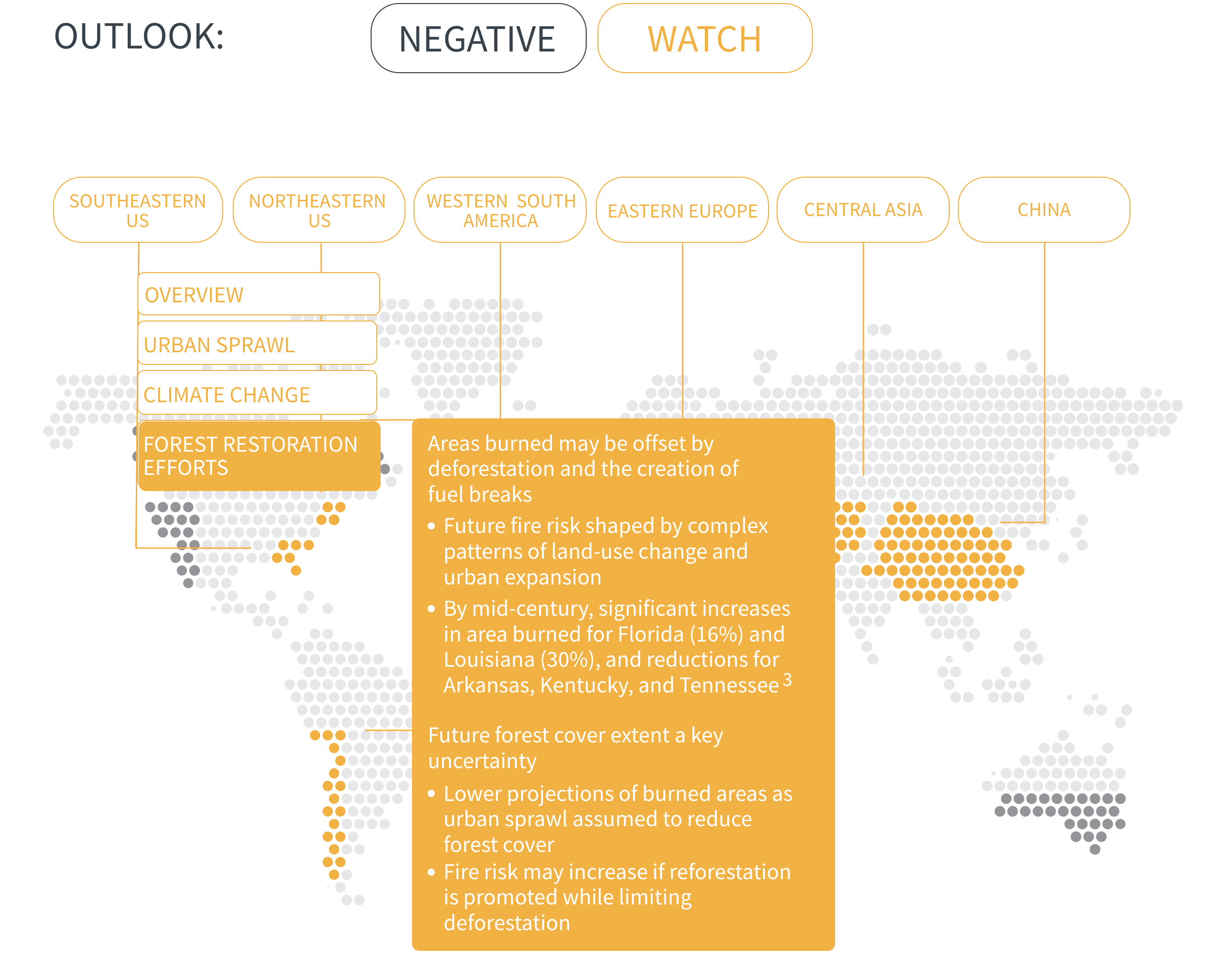
As urban developments around the world creep further into wildlands, the number of people and value of assets exposed to wildfire will increase. This compounds risk in regions already prone to wildfires and creates new risks where wildfire activity is not yet a problem but may become one as climate change progresses.
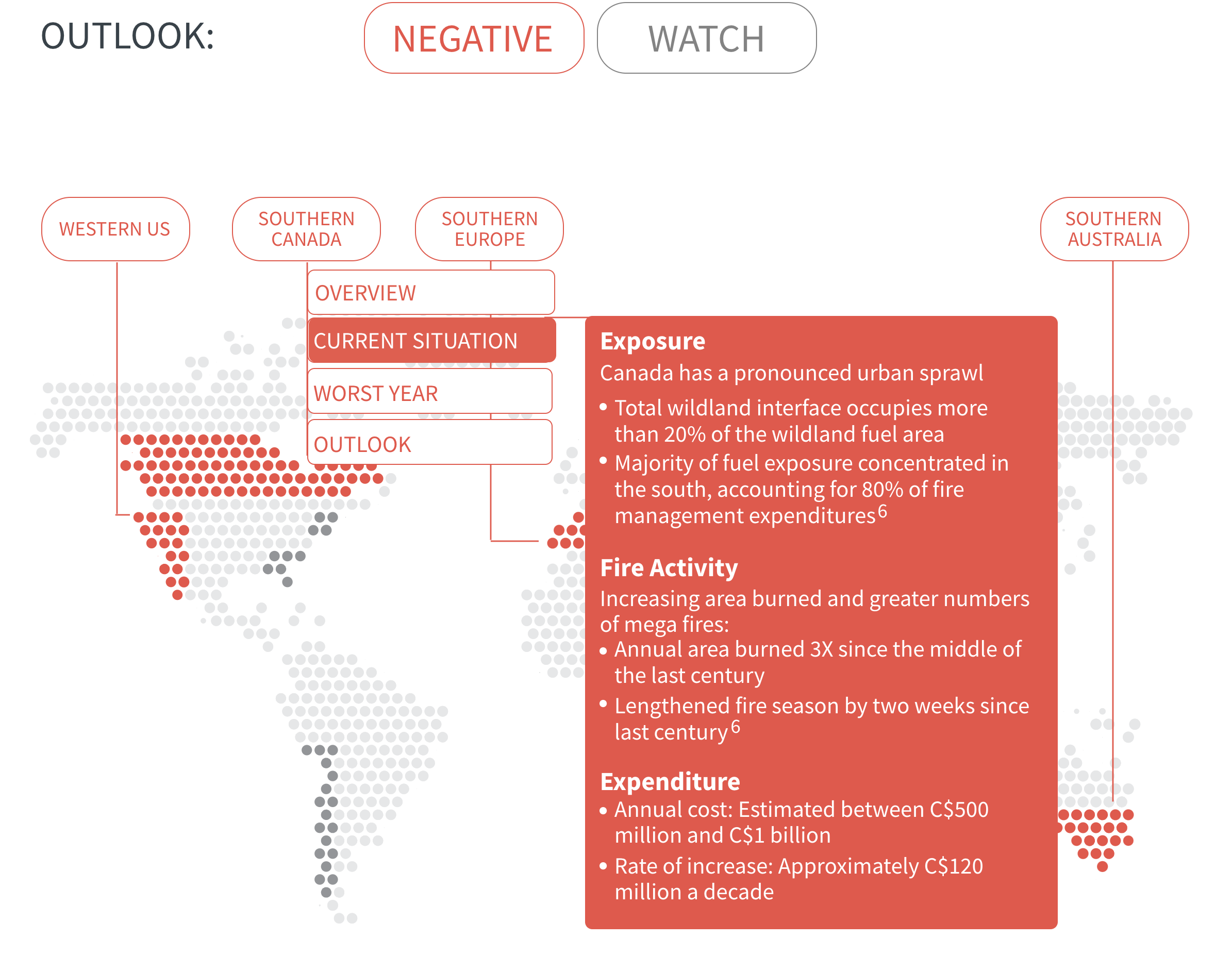
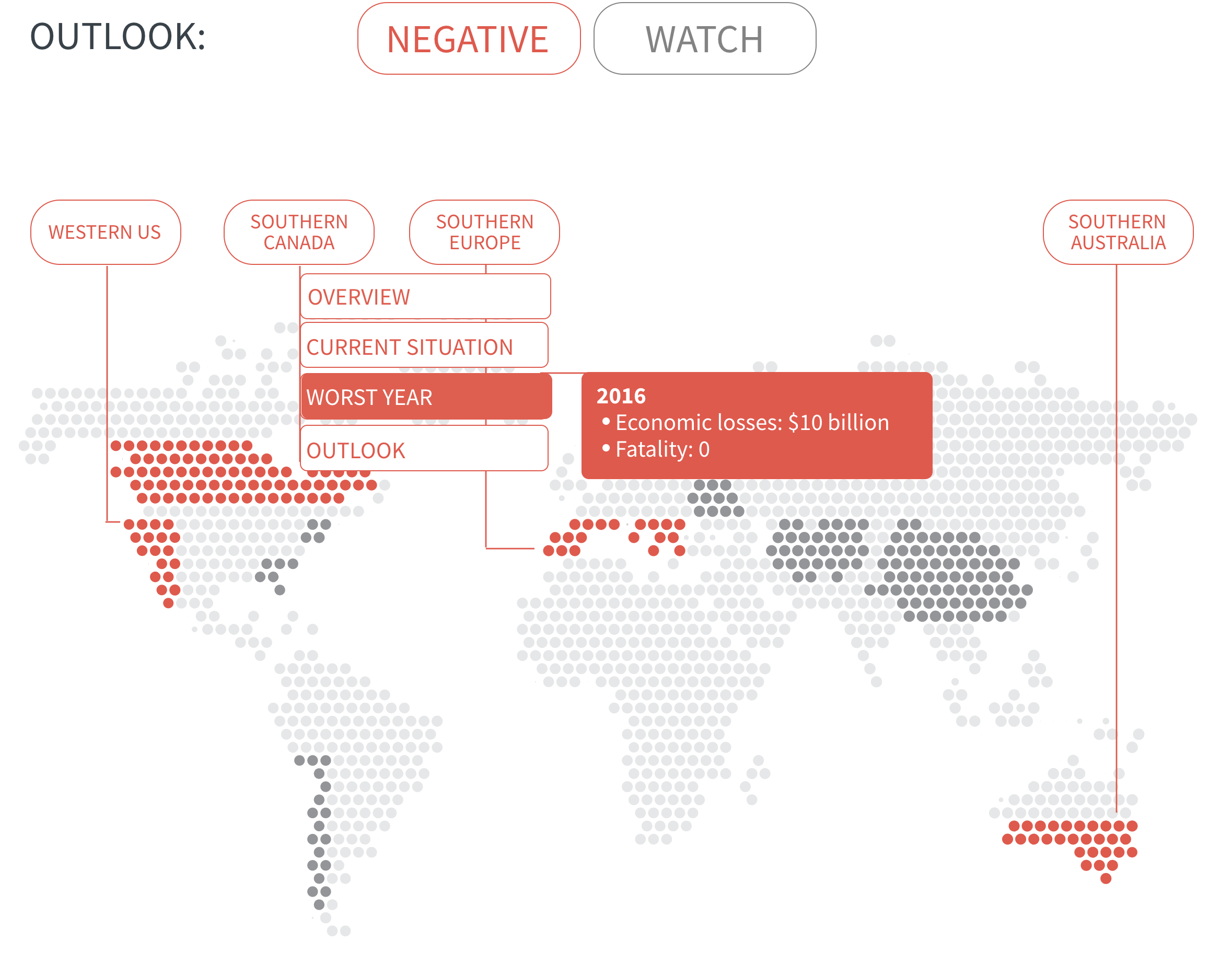
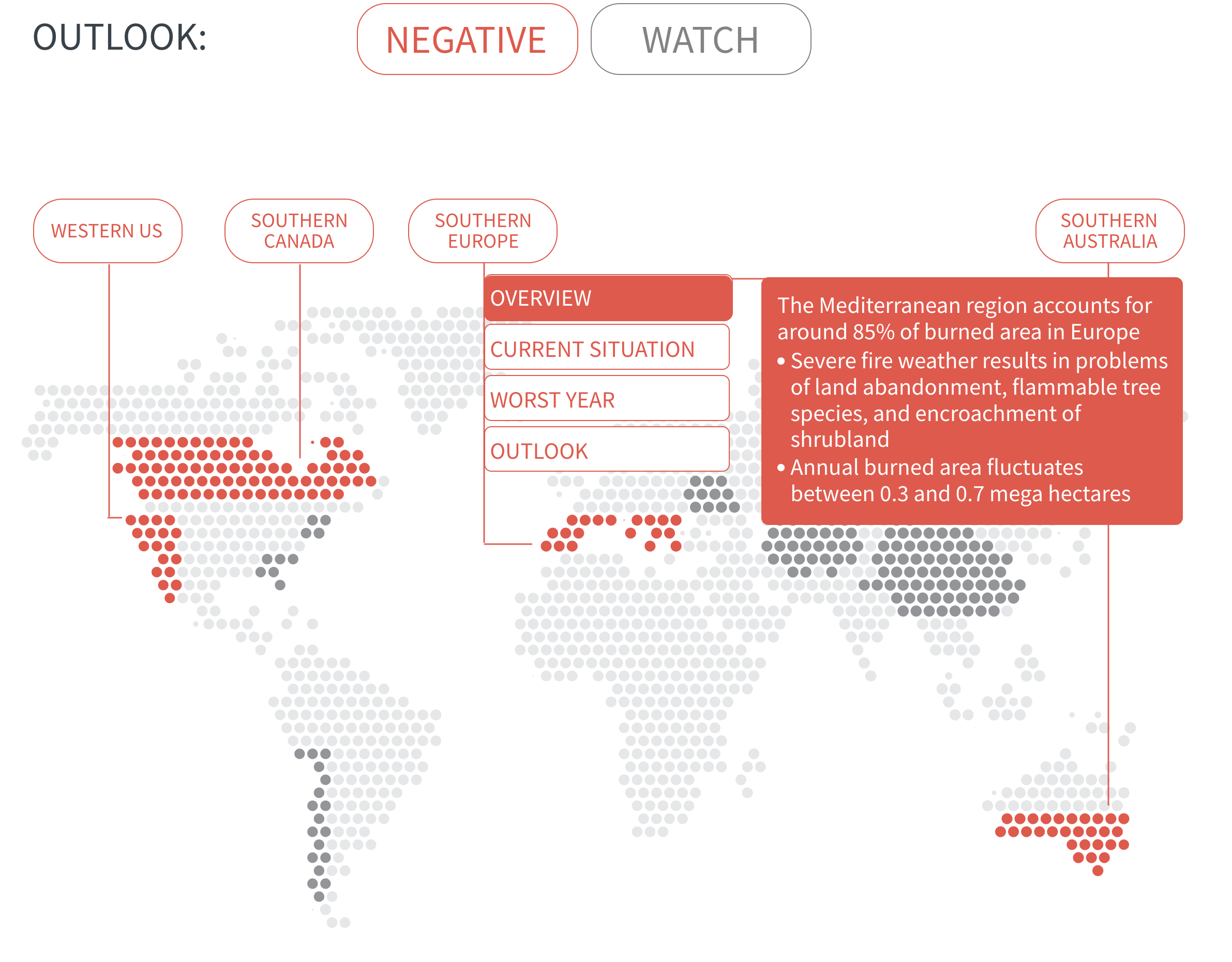
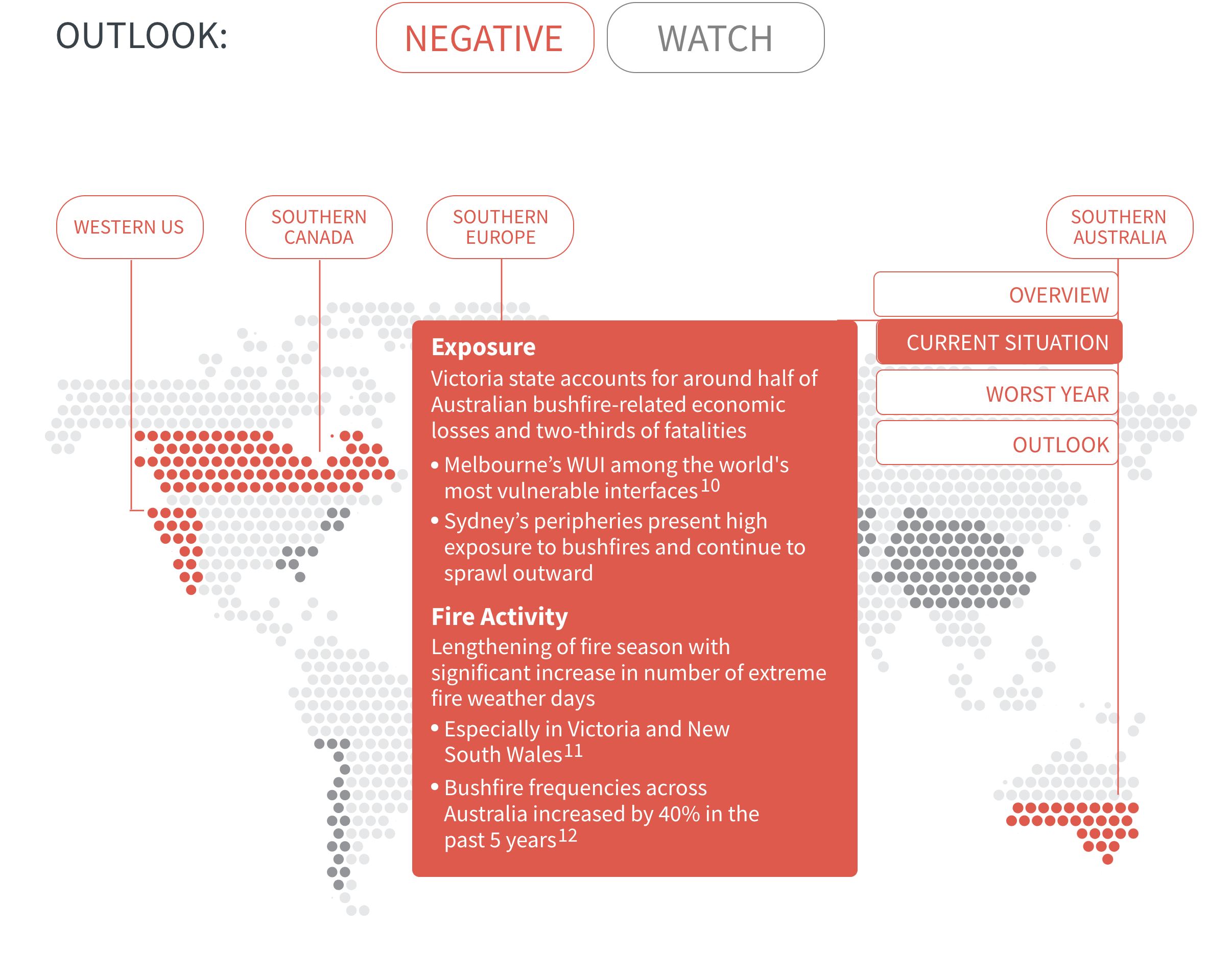
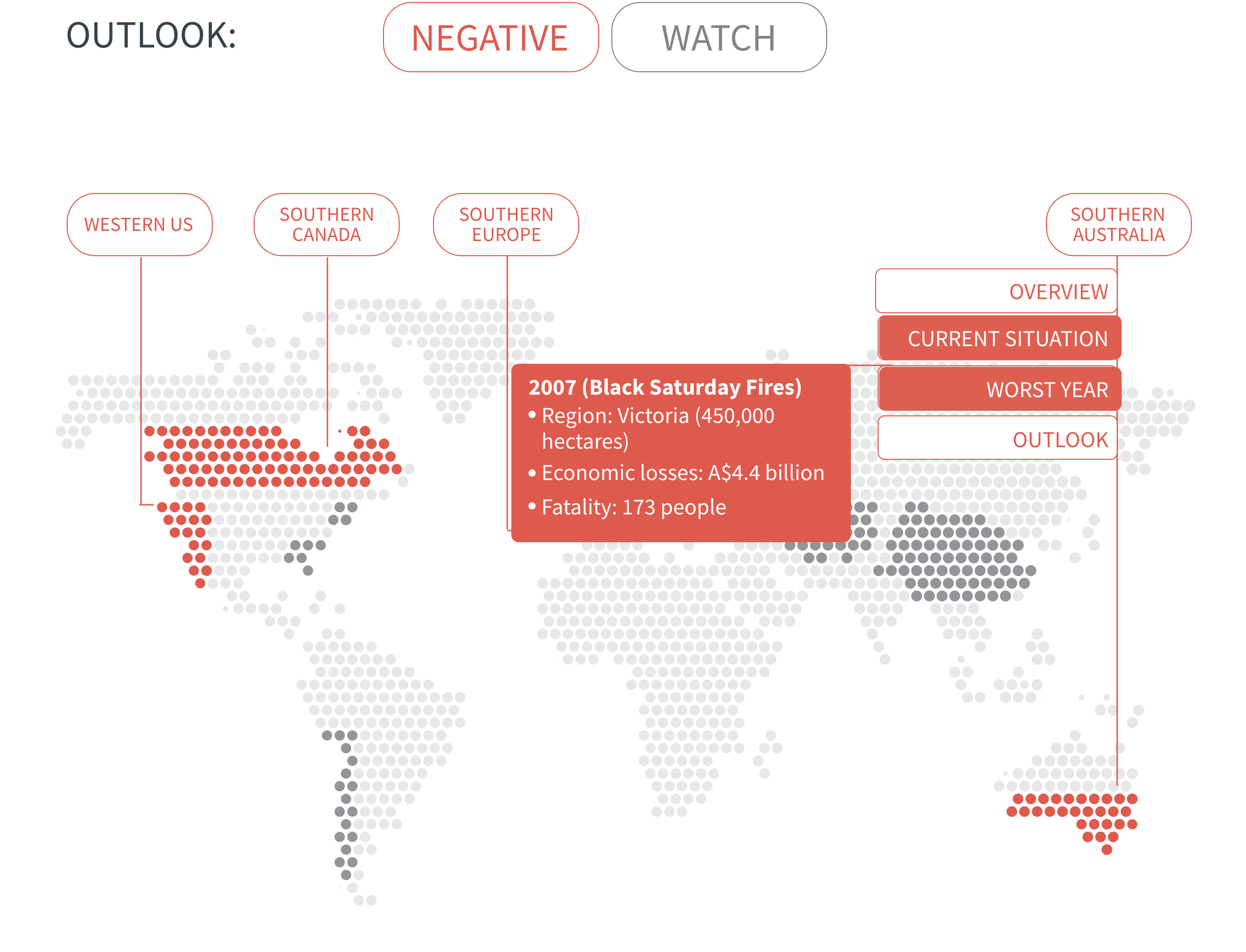
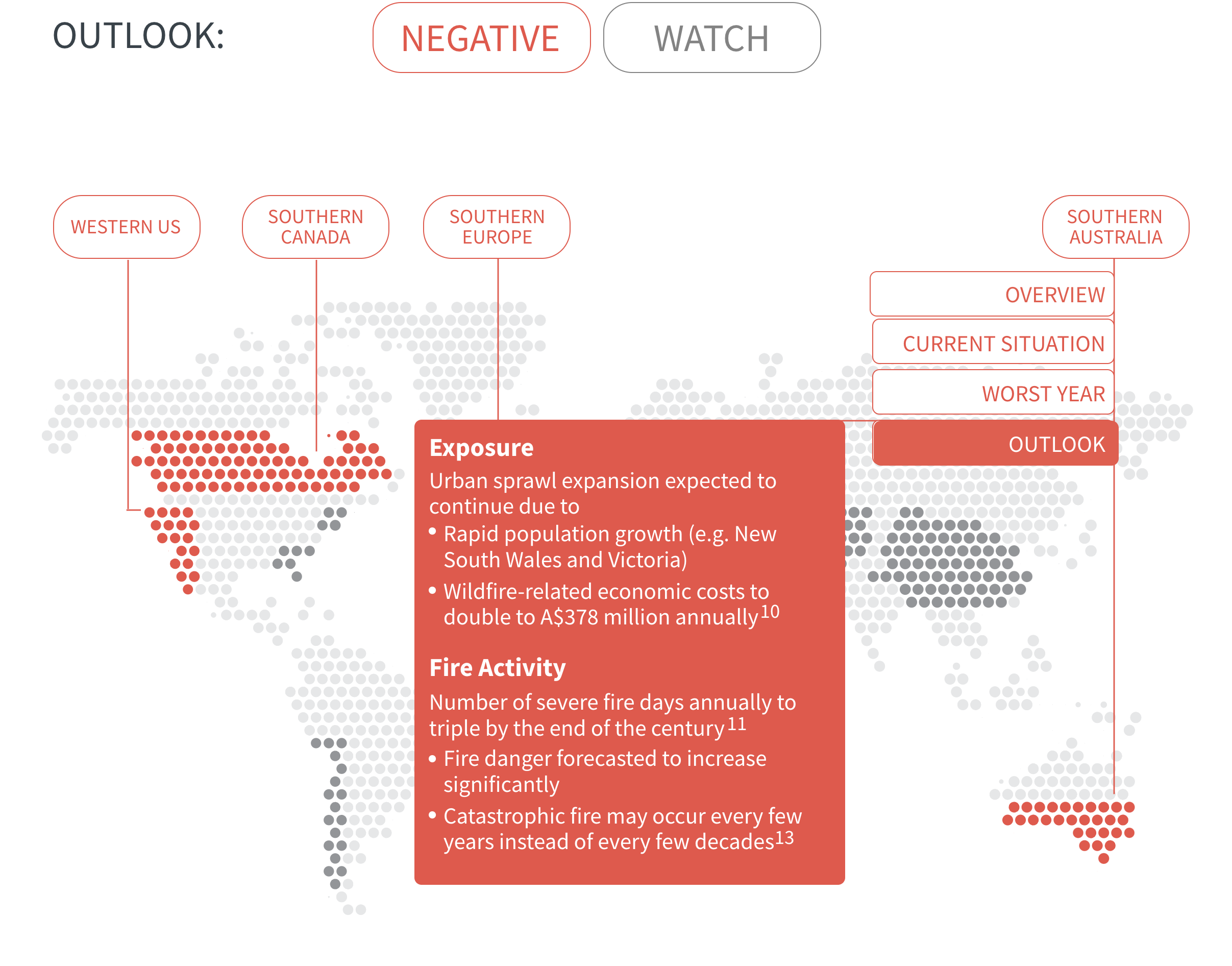
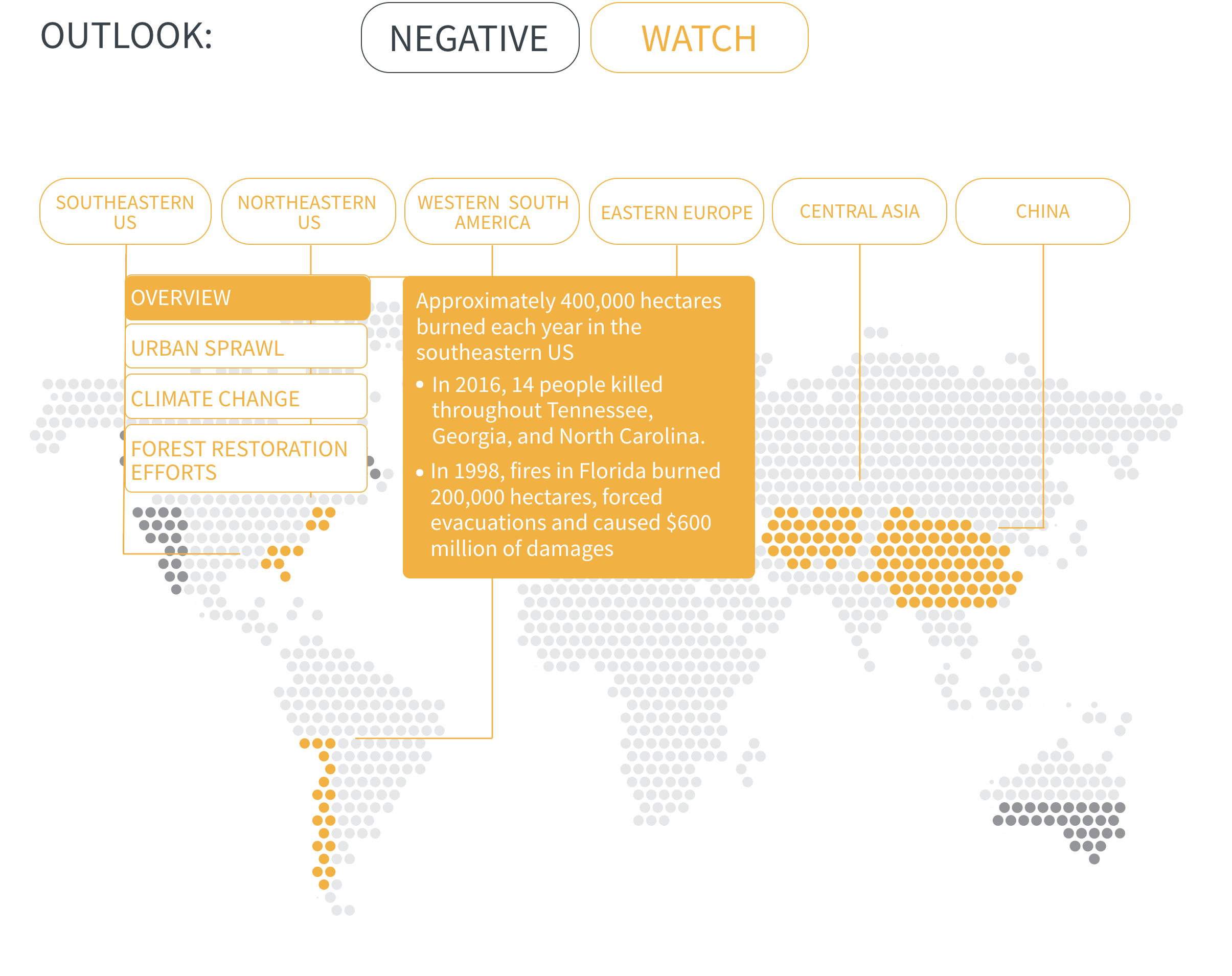
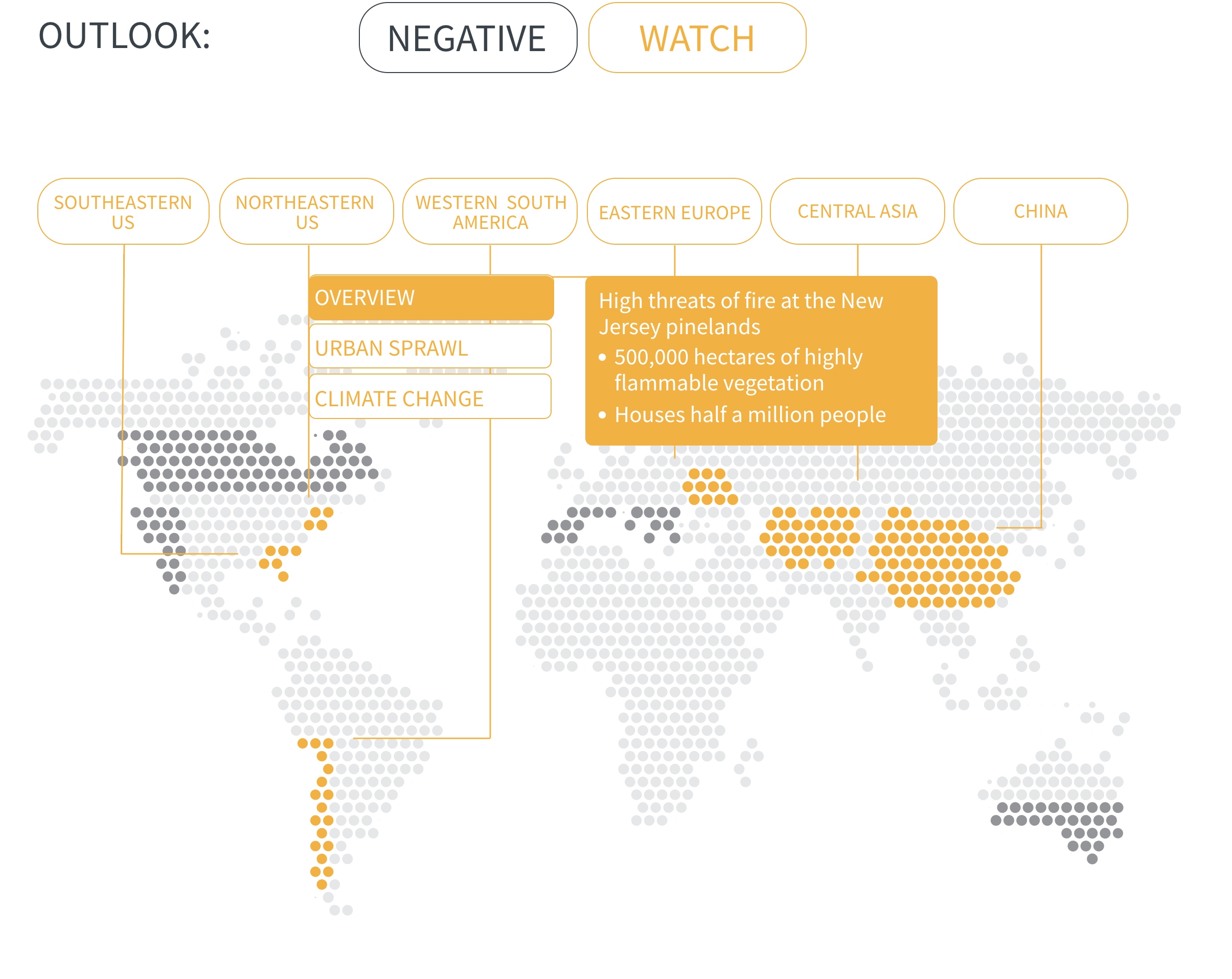
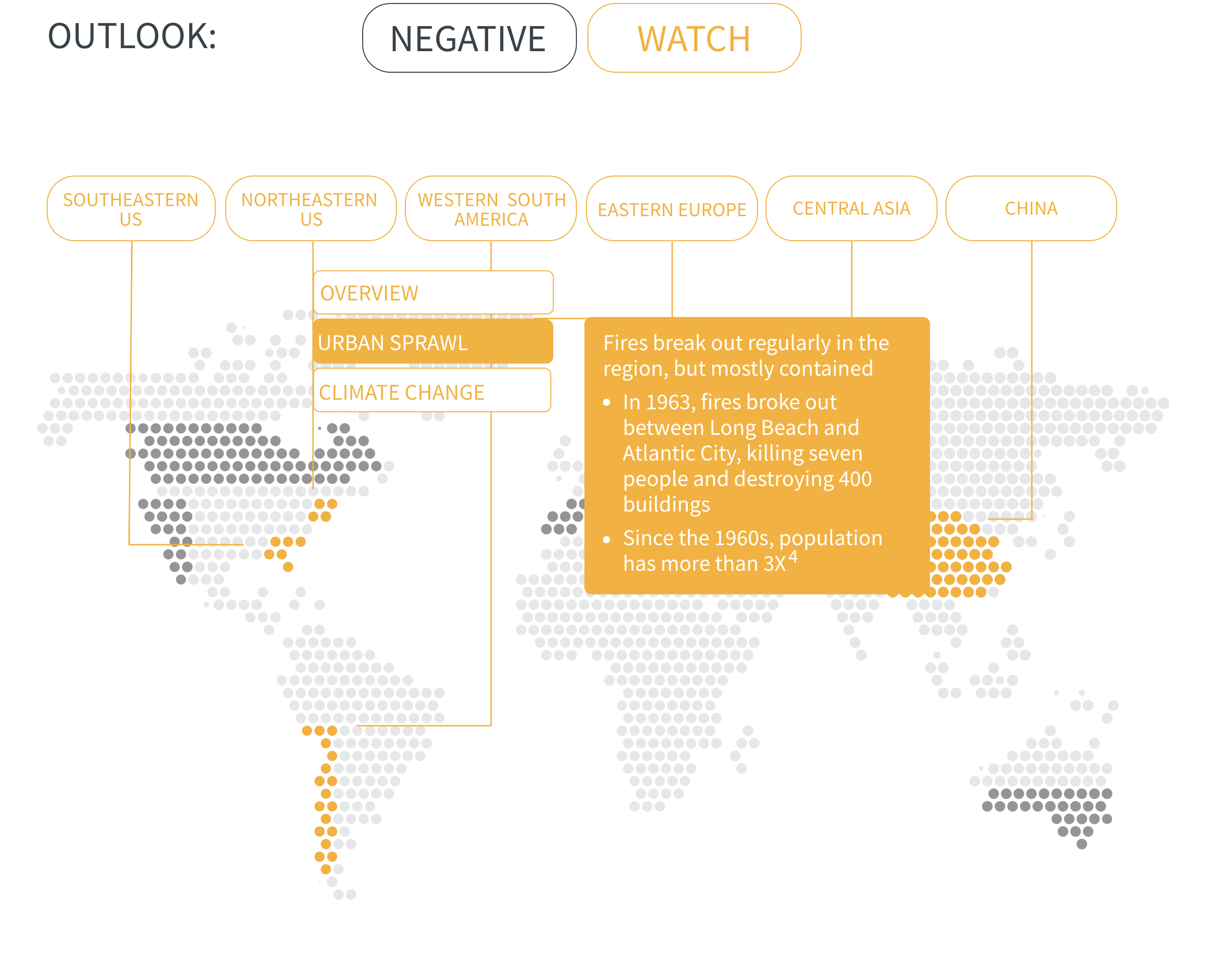
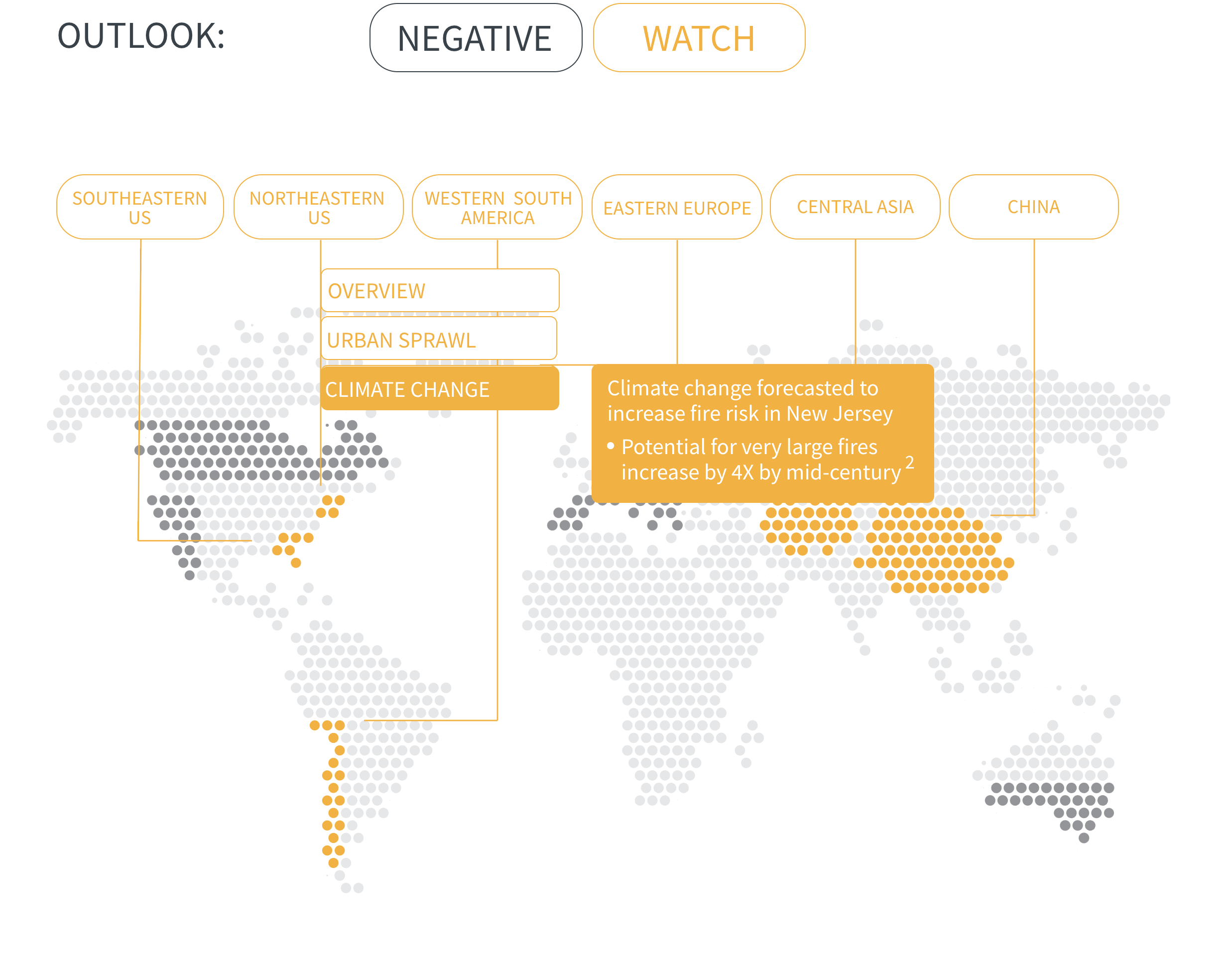
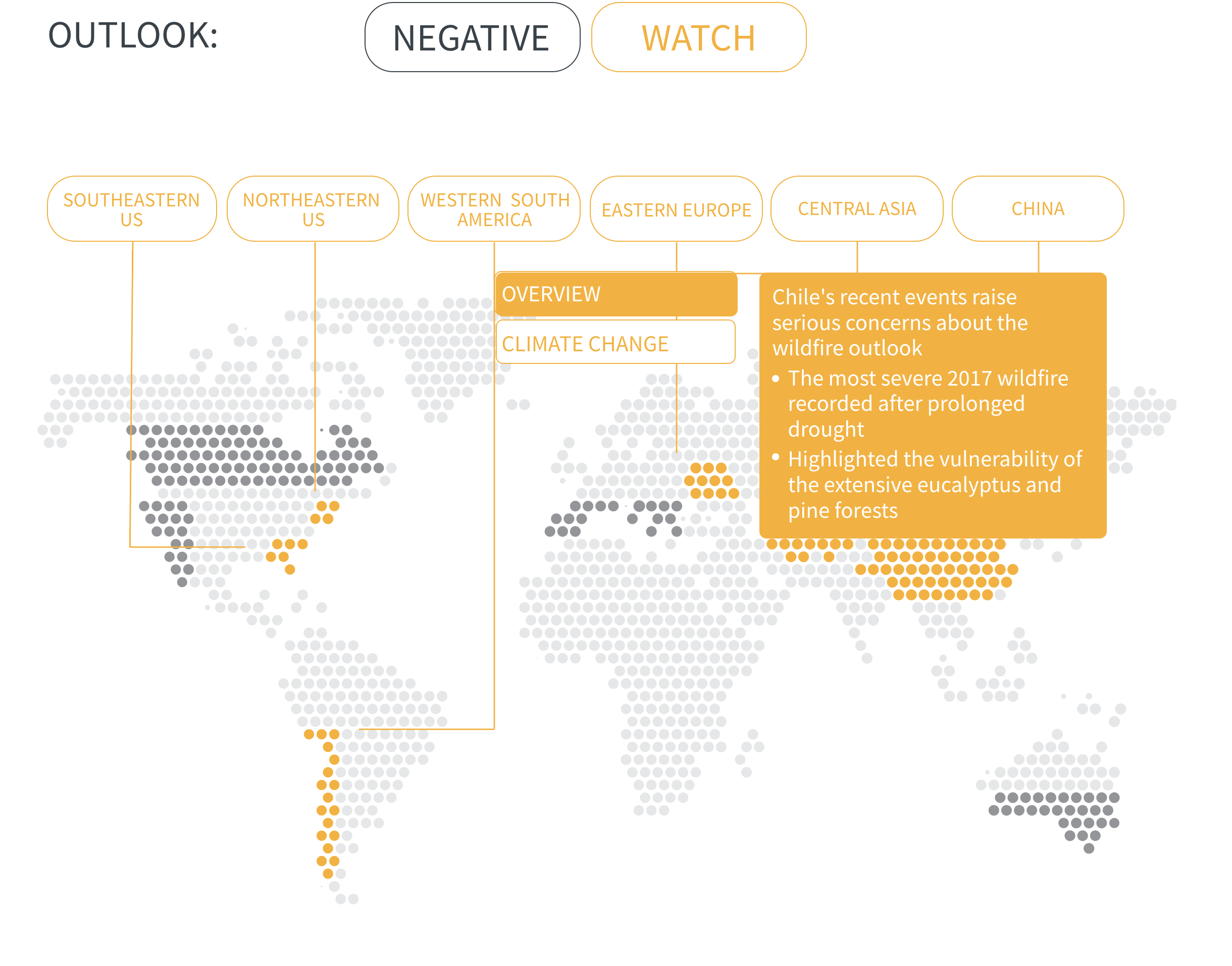
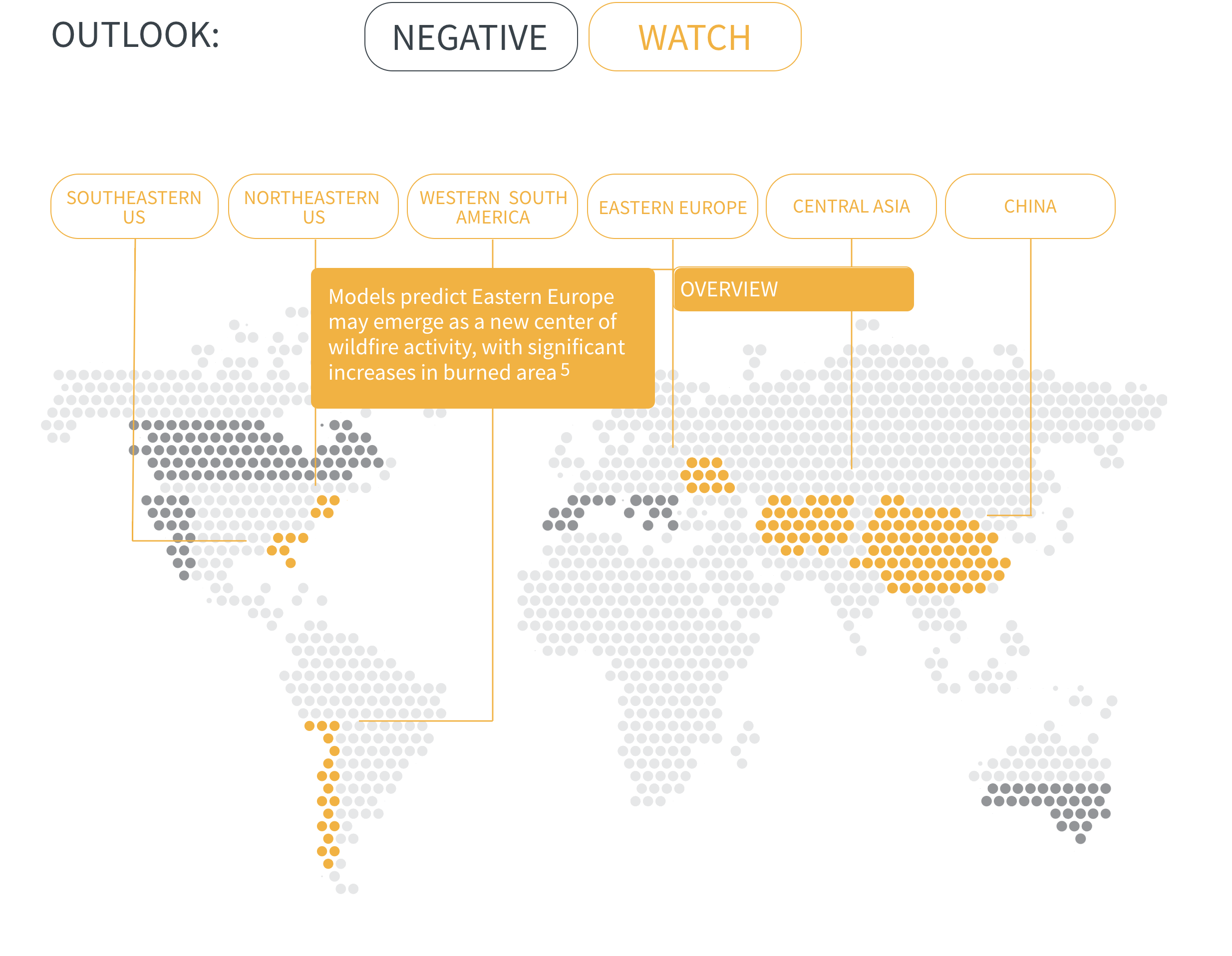
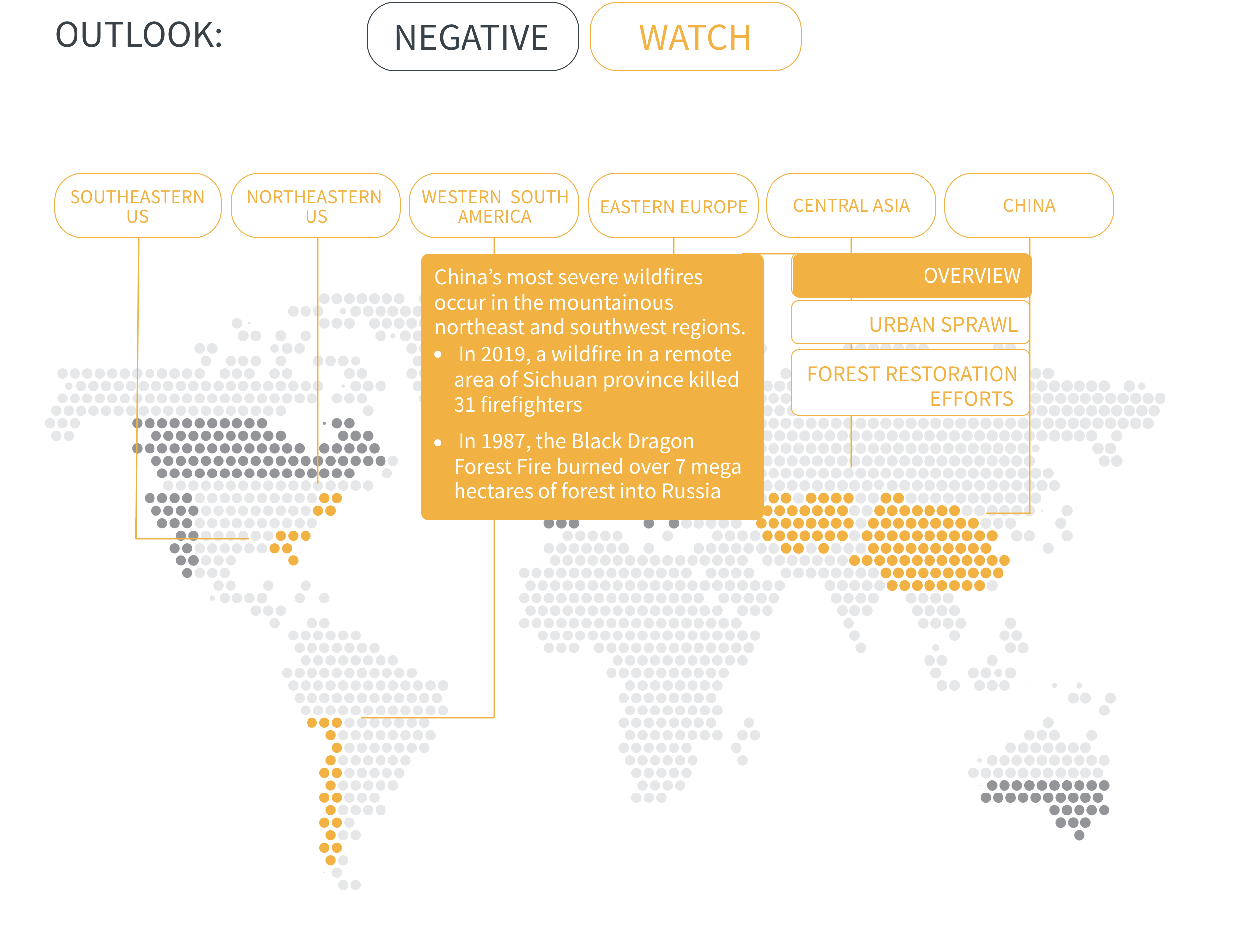
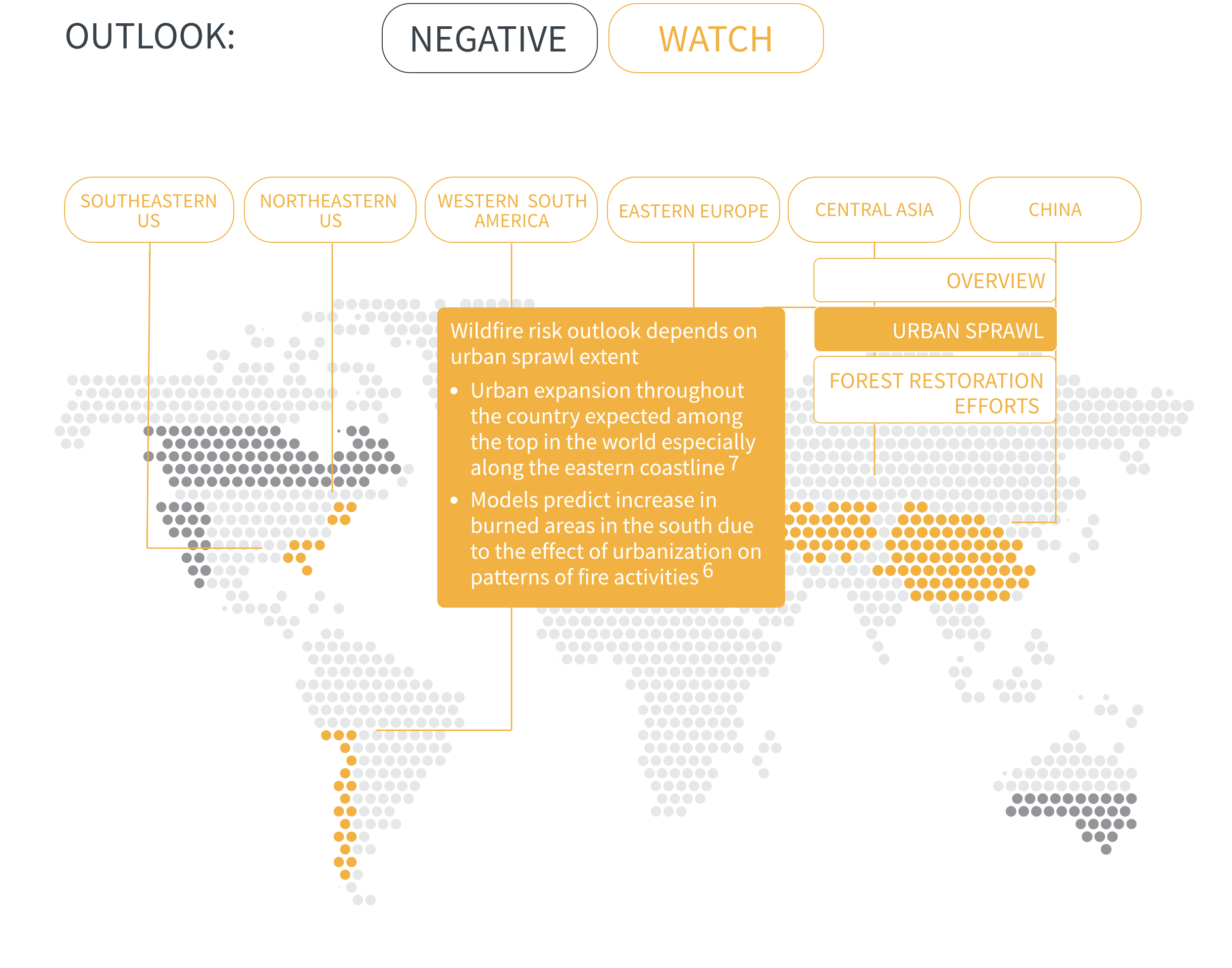
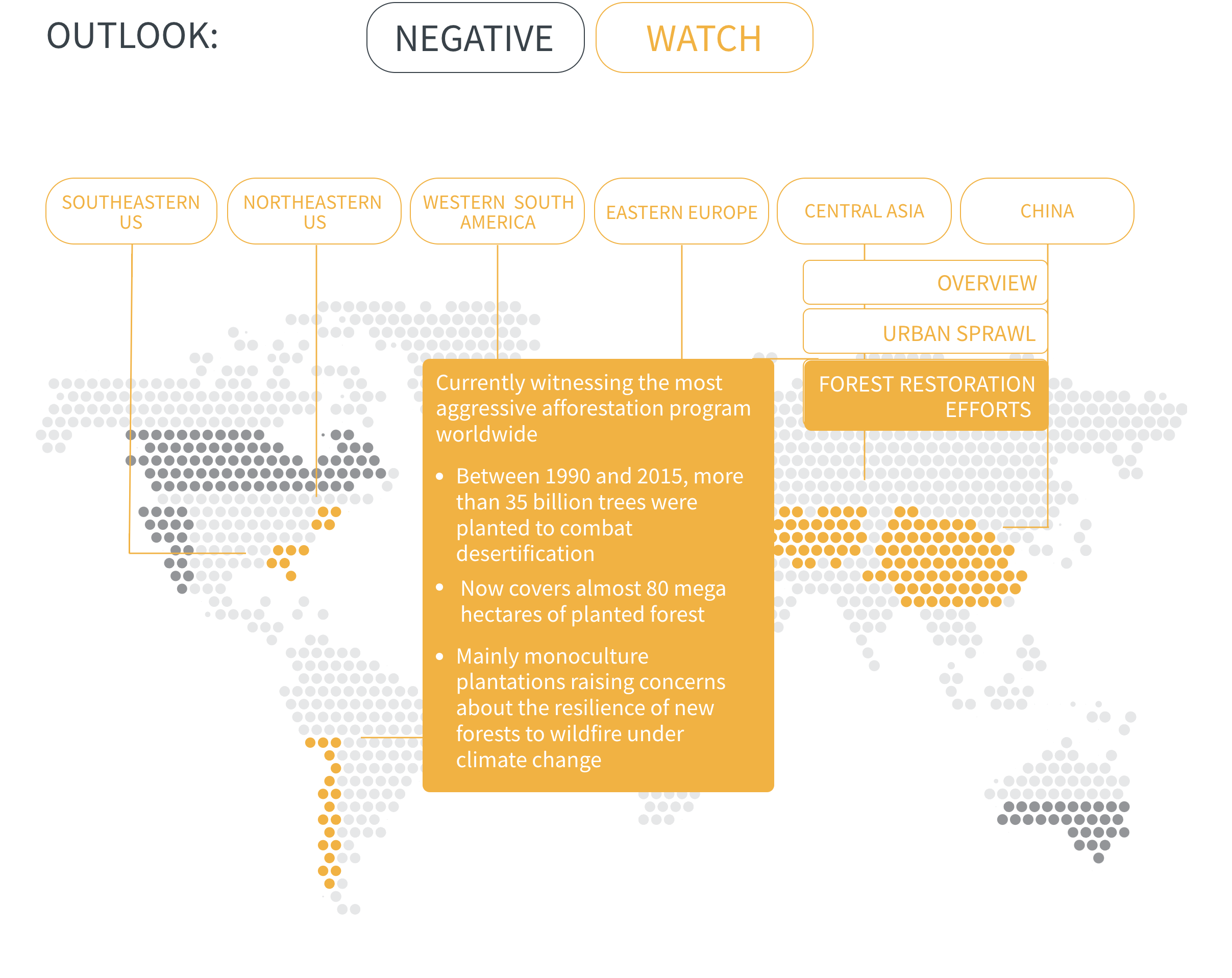
Regional Outlook The interactive map identifies areas with a ‘Negative’ outlook as well as those under ‘Watch.’ Click on a region to learn more about its exposure, fire activity, expenditure, future outlook and more.
Regions with a ‘Negative’ outlook are characterized by high levels of current risk and well-established trends in underlying climate and exposure drivers. These regions will likely face greater wildfire risk in the coming decades. Regions under ‘Watch’ have lower levels of current risk but have climate and/or exposure trends that provide cause for concern. There may be early indications of deteriorating risk.
Preparing for increased wildfire risk
Wildfire risk is set to increase in many regions of the world, as populations continue to expand into wildland areas and as climate change increases fire activity. Risk management will need to be tailored to the landscape, type of fuels, and the prevailing climatological characteristics. However, the experiences of countries already dealing with serious wildfires offer some valuable lessons:
- Adopt a risk-based approach to fire management
- Break out of the firefighting trap
- Build resilient communities
- Get incentives right
- Leverage risk transfer mechanisms such as cat bonds and parametric insurance